
THE VOICE OF INTERNATIONAL LITHUANIA
|
VilNews has its own Google archive! Type a word in the above search box to find any article.
You can also follow us on Facebook. We have two different pages. Click to open and join.
|
The Polish-Lithuanian
War 1919-1920
A series of articles in 4 parts
By Vincas Karnila, Associate editor
vin.karnila@VilNews.com

South-eastern Lithuania, Vilnius included, was occupied by Poland during the interwar period.
Picture: Celebration of the incorporation of Vilnius Region to Poland, 1922.
The Polish–Lithuanian War was an armed conflict between Lithuania and Poland in the aftermath of World War I and Lithuania's declaration of independence 16 February 1918.
The conflict primarily concerned territorial control of the Vilnius Region, including Vilnius, and the Suwałki Region, including the towns of Suwałki, Augustów, and Sejny. According to Lithuanian historians, the war was part of the Lithuanian Wars of Independence and spanned from spring 1919 to November 1920. According to Poland, the war included only fighting over the Suwałki Region in September–October 1920 and was part of the Polish–Soviet War.
After Vilnius was occupied by the Russian Bolsheviks in 1919, the government of the Republic of Lithuania established its main base in Kaunas. When Vilnius was forcibly annexed by Poland, Kaunas became the temporary capital of Lithuania, a position it held until 28 October 1939, when the Red Army handed Vilnius back to Lithuania. The Constituent Assembly of Lithuania first met in Kaunas on 15 May 1920. There were no diplomatic relations between Poland and Lithuania until 1938.
 |
Part 1 – THE BUILD UP World War I ended on November 11, 1918 when Germany signed the Compiègne Armistice. On November 13, Soviet Russia renounced the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk. Most of today's Poland, Belarus, Ukraine and the Baltic States were passed to the government of Germany, which in turn decided to grant these states limited independence as buffer states) and began the Soviet westward offensive of 1918–1919. |
 |
Part 2 – ADVANCES and RETREATS In April 1920 Poland launched the large-scale Kiev Offensive in hopes to capture Ukraine. Initially successful, the Polish Army started retreating after Russian counterattacks in early June 1920. Soon the Soviet forces began to threaten Poland's independence as they reached and crossed the Polish borders. |
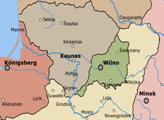 |
Part 3 – STRUGGLES for the VILNIUS REGION Polish chief of state Jozef Pilsudski ordered his subordinate, General Lucjan Zeligowski, to stage a mutiny with his 1st Lithuanian–Belarusian Division (16 battalions with 14,000 soldiers) in Lida and capture Vilnius in fait accompli. |
 |
Part 4 – THE AFTERMATH In March 1921, the plans for a referendum vote were abandoned. Neither Lithuania, which was afraid of a negative result, nor Poland, which saw no reason to change status quo, wanted it. The parties could not agree in which territory to carry out the vote and how Żeligowski's forces should be replaced by the League's forces. The League of Nations then moved on from trying to solve the narrow territorial dispute in the Vilnius Region to shaping the fundamental relationship between Poland and Lithuania. |
- Bookmark :
- Digg
- del.icio.us
- Stumbleupon
- Redit it
VilNews e-magazine is published in Vilnius, Lithuania. Editor-in-Chief: Mr. Aage Myhre. Inquires to the editors: editor@VilNews.com.
Code of Ethics: See Section 2 – about VilNews. VilNews is not responsible for content on external links/web pages.
HOW TO ADVERTISE IN VILNEWS.
All content is copyrighted © 2011. UAB ‘VilNews’.

 Click on the buttons to open and read each of VilNews' 18 sub-sections
Click on the buttons to open and read each of VilNews' 18 sub-sections 



This posting is magnificent and what a excellent studies which you have finished. It has helped me masses. Thank you very lots.
[…] During the interwar period between First and Second World Wars the political leadership of reconstituted Poland aspired to a European great power status and conducted a policy of territorial expansion against its neighboring countries. As a result of several military campaigns in 1919-1920, Poland acquired considerable territories inhabited by non-Polish populations [see our VilNews articles on the Polish/Lithuanian war 1919-1920 at https://vilnews.com/?p=11551%5D. […]