
THE VOICE OF INTERNATIONAL LITHUANIA
|
VilNews has its own Google archive! Type a word in the above search box to find any article.
You can also follow us on Facebook. We have two different pages. Click to open and join.
|
Article 1 of 6

Situation plan created by and property of Castle Research Center Lithuanian Castles. All rights reserved
In 1944, the Soviet Union drove the army of Nazi Germany from the territory of Lithuania and occupied the country for a second time. Repressions against the citizens of our country began without delay. Members of the anti-Soviet armed resistance and underground anti-Soviet organisations, their supporters, farmers, teachers, intelligentsia; politicians, public servants, soldiers, and other officials of former independent Lithuania; and members of the Catholic clergy were arrested, imprisoned, exiled, sentenced to death, and subsequently executed. The convicts were judged by Military Tribunals of internal troops and an Extraordinary Meeting with the State Security Minister of the USSR. Pursuant to the 1926 Criminal Code Article 58 of RSFSR, they imposed penalties which included custody or the death sentence (by shooting). Indictments were based on torture or documents obtained illegally. Between 1944 and 1953, the Extraordinary Meeting convicted at least 11,932 people and the Military Tribunals – at least 22,080.
CONSEQUENCES OF THE TOTALITARIAN REGIME
IN LITHUANIA 1940–1953.
In 1939, the Soviet Union and Nazi Germany signed a secret agreement (the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact) for the division of Central and Eastern Europe. Lithuania fell under the sphere of influence of the Soviet Union, as a result, on 15 June 1940 Lithuania was occupied and subsequently annexed by the USSR. In order to carry out the sovietisation of the country, to break and destroy it, physical and spiritual destruction of the nation took place. The scheme was prepared by the top Communist Party officials of the Soviet Union and implemented by the repressive NKVD–MVD and NKGB–MGB structures and subordinate courts – Military Tribunals of the USSR NKVD troops and the non-judicial authority, the Extraordinary Meeting of the People’s Commissariat of Internal Affairs of the USSR. These institutions carried out the instructions of Communist Party officials by surveilling, arresting, investigating, imprisoning, and killing “traitors of the motherland”. During the first Soviet occupation in 1940, 23,000 Lithuanian citizens were arrested, executed, or exiled.
From the end of June 1941, when the country was occupied by the military forces of Nazi Germany until 1944, nearly 30,000 Lithuanian citizens were arrested and deported to concentration camps, another 60,000 were taken for forced labour in Germany, and 240,000 were killed, approximately 200,000 of them Jews.
In 1944, the Soviet Union drove the army of Nazi Germany from the territory of Lithuania and occupied the country for a second time. Repressions against the citizens of our country began without delay. Members of the anti-Soviet armed resistance and underground anti-Soviet organisations, their supporters, farmers, teachers, intelligentsia; politicians, public servants, soldiers, and other officials of former independent Lithuania; and members of the Catholic clergy were arrested, imprisoned, exiled, sentenced to death, and subsequently executed. The convicts were judged by Military Tribunals of internal troops and an Extraordinary Meeting with the State Security Minister of the USSR. Pursuant to the 1926 Criminal Code Article 58 of RSFSR, they imposed penalties which included custody or the death sentence (by shooting). Indictments were based on torture or documents obtained illegally. Between 1944 and 1953, the Extraordinary Meeting convicted at least 11,932 people and the Military Tribunals – at least 22,080.
Between 1944 and 1953, around 186,000 people were arrested and imprisoned, of which 143,000 were imprisoned in GULAG camps, 118,000 – exiled, and nearly 21,000 members of the armed anti-Soviet resistance and their supporters perished.



Soviet Gulag camps
Editors note - The Gulag (Russian: ГУЛаг, tran. GULag) was the government agency that administered the main Soviet forced labor camp systems. GULag is the acronym for Chief Administration of Corrective Labor Camps and Colonies (Russian: Гла́вное управле́ние исправи́тельно-трудовы́х лагере́й и коло́ний, tran. Glavnoye upravlyeniye ispravityel'no-trudovih lagyeryey i koloniy) of the NKVD. It was officially created on April 25, 1930 and dissolved on January 13, 1960.
Prior to the collapse of the Soviet Union, the procedure for carrying out the most severe sentence – death by shooting – as well as the place of burial were classified as a state secret. In 1990, after the re-establishment of independence in Lithuania, it became known an appropriate burial place for the bodies of the executed convicts. General-Lieutenant Ivan Tkachenko, the person designated by the NKVD–NKGB for the Lithuanian SSR, had in 1944 selected the grounds of the former Tuskulėnai Manor as the site that complied with all the security requirements of the time. In this 1.3 ha territory near the city centre surrounded by a high brick and timber fence it was easy to safely hide the burial sites of the bodies. The MGB documents from 1952 specify that Tuskulėnai was selected “due to the impossibility of driving outside the city limits at night as the situation in the Lithuanian SSR was extremely tense”. There was still armed anti-Soviet resistance and therefore there was fear of clashes with freedom fighters while moving the corpses for burial. Another important circumstance was the experience of 1941 when, at the outset of the war between Germany and the USSR, retreating security agents did not have time and did not manage to conceal the execution sites. In summer and autumn 1941, graves of people executed in the NKVD internal prison were identified in Kaunas Petrašiūnai Cemetery.
This is the translation of a certificate dated 23 June 1952 by Lieutenant-Colonel Pavel Grishin, head of the Lithuanian SSR MGB Division, about the reasons why the grounds of the former Tuskulėnai Manor were selected in 1944 for burying the bodies of people executed in the Lithuanian SSR NKGB–MGB internal prison between 1944 and 1947. The place name Tuskulėnai is not mentioned in the certificate.
|
79 Certificate From the time the Lithuanian SSR was liberated from the German fascist invaders until 1947 when, following the order of the Presidium of the Supreme Council of the USSR, the death penalty was abolished, those who were shot were buried in the territory of a former private estate of the style of the country residence within Vilnius city limits. The location is marked with the arbitrary sign (+) on the enclosed city plan. Around 1.000 people are buried in the territory of this estate. Burial within the city limits and the use of the said estate for this purpose was sanctioned, due to the extremely tense situation in the republic, by Lieutenant- General Tkachenko, the person formerly designated by the USSR MVD–MGB for the Lithuanian SSR following the request by Lieutenant-Colonel Kharchenko, former head of the Lithuanian SSR MGB Division A. Two residential buildings of the estate were passed to DOSAAF in 1949, therefore the burial site remains without the necessary protection and this shortcoming has not been eliminated since. In order to eliminate this shortcoming, it is necessary to build a small summer house on the said part of the estate and accommodate one of our employees in it. Head of the Lithuanian SSR MGB Division A 23 June 1952 The said certificate was issued on the instruction of the Minister Major- General Kaldanov on his arrival to the Lithuanian SSR and returned on his departure from the Lithuanian SSR. Head of the Lithuanian SSR MGB Division A 14/07/1952 (Grishin) /Signature/
Translation property of the Memorial Complex of the Tuskulėnai Peace Park. All rights reserved. |
This is the translation of a letter dated 19 February 1952 from Lieutenant-Colonel Pavel Grishin, head of the Lithuanian SSR MGB Division, to Major-General Arkady Gertsovsky, head of the USSR MGB Division A, regarding the opportunity to destroy the remains of the bodies on the grounds of Tuskulėnai Manor using chemical products.
|
K Series STRICTLY PRIVATE 59 Division A 19 February 1952 10/7/1-3314 /Signature/ To the HEAD OF DIVISION A of USSR MGB Major-General GERTSOVSKY Moscow In 1944, i.e. prior to my arrival to work in Lithuania, the location for the burial of those who received the highest sentence was selected within Vilnius city limits due to the impossibility of driving outside the city limits at night as the situation in the Lithuanian SSR was extremely tense. We were to use this site until 1947, i.e. when, following the order of the Presidium of the Supreme Council of the USSR, the death penalty was abolished and this place has not been used since. Today, there is an opportunity to liquidate this burial site, but we cannot do it, i.e. evacuate the remains to another location, due to the cold weather which recurs each winter. For this reason, could you clarify the possibility of liquidating this location using chemical products, specifically so as not to attract the attention of outsiders and how could this be taken care of, i.e. how would we carry it out.
Head of the Lithuanian SSR MGB Division A Lieutenant-Colonel /Signature/ (Grishin) 2 copies printed 1 – addressee 2 – __________ Executed by Grishin Printed by Dmitriyeva /Handwritten note: Note: Lieutenant-Colonel Vorobev, head of Division A of the Lithuanian SSR MGB transmitted via a HF (high frequency) connection that the remains cannot be evacuated and it is categorically forbidden to do so. Additional notification is required for elimination of the burial site of the remains using chemical products. 05/03/1952 /Signature/
|

Photo property of the Lithuanian Special Archives. All rights reserved.
Lieutenant-Colonel Pavel Grishin
People executed in the NKGB–MGB internal prison and participants of the anti-Soviet underground movement tortured or killed during NKVD counterinsurgency operations in Vilnius and its environs, were buried within the grounds of Tuskulėnai until the late spring of 1947 when the death penalty was abolished in the USSR. At the beginning of 1950, the Presidium of the Supreme Council of the USSR passed the decree “On the employment of the death penalty for traitors of the motherland, spies, and saboteurs-subversives”, as a result of which the death penalty, pursuant to the 1926 Criminal Code Article 58 of RSFSR, was re-instated and the execution resumed. Most were carried out in the same NKGB–MGB internal prison as before and continued until 1961. Executions continued after 1961 but they were not carried out pursuant to the 1926 Criminal Code Article 58 of RSFSR. You would need to look at each and every individual execution that took place after 1961 to determine on what basis they were carried out.
Today, the burial sites of those executed after the re-instatement of the death penalty,
still remain a secret.
Tuskulėnai is the only known location where the bodies of those executed in Vilnius NKGB–MGB internal prison were buried, and therefore it has become one of the symbols commemorating the victims of the Soviet terror.
MGB – rus. МГБ, Министерство государственной безопасности – Lith. Valstybės saugumo ministerija – Ministry of State Security [of the USSR]
MVD – rus. МВД, Министерство внутренних дел – Lith. Vidaus reikalų ministerija – Ministry of Internal Affairs [of the USSR]
NKGB – rus. НКГБ, Народный Комиссариат Государственной Безопасности – Lith. Valstybės saugumo liaudies komisariatas – People’s Commissariat for Internal Affairs [of the USSR]
NKVD – rus. НКВД, Народный комиссариат внутренних дел – Lith. Vidaus reikalų liaudies komisariatas – People’s Commissariat of Internal Affairs [of the USSR]
Lithuanian SSR – Lithuanian Soviet Socialist Republic
RSFSR – the Russian Soviet Federal Socialist Republic
USSR – Union of Soviet Socialist Republics
Bronius Eiva was a Lithuanian partisan leader. He was arrested 8 September 1944. He is one of the many that between 28 September 1944 and 16 April 1947 that were executed in the NKGB–MGB internal prison in Vilnius and then buried in the mass graves at Tuskulėnai.
This is a translation of excerpts from the letter of farewell Bronius Eiva wrote to his wife, dated September 1944, written from the prison of Ukmergės People’s Commissariat for Internal Affairs, where severely wounded, he was being investigated after his arrest on 8 September 1944.
“This is my last letter. I shall die and you shall live. Please raise our precious daughter Rūtelė-Regina, and when she grows up please tell her I loved her…I lay wounded in the right leg. But it is not the pain that bothers me most, it is the sorrow for you…Please find out when I was shot or hanged and where they bury me. Dig me up and take me to Šeta cemetery.”
TUSKULĖNAI MASS GRAVES
Starting in autumn 1944, death penalties passed by Military Tribunals of the USSR and the Extraordinary Meeting were carried out in the NKGB–MGB internal prison in Vilnius (now – Gedimino pr. 40 / Aukų g. 2A). Between 28 September 1944 and 16 April 1947, the death penalty was carried out on 767 people; 613 of them were sentenced under Articles 58(I)(a) and 58(I)(b) ‘For treason’ of the 1926 Criminal Code of the RSFSR (Статья 58 Уголовного Кодекса РСФСР/вариант 1926 года). Under these articles, people were charged for actions which sabotage the military power of the USSR, its independence as a country, and sanctity of its territory.
In 1944, the death penalty was carried out on 45 convicts
In 1945 – on 479 convicts
In 1946 – on 185 convicts
In 1947 – on 58 convicts.
The largest number of executions, 45 people, was carried out on 21 March 1945. After the executions, the bodies were secretly buried within the grounds of Tuskulėnai Manor.
The convicts included;
Participants of the anti-Soviet movement
Participants of the uprising of 23 June 1941
Fighters of the Polish Armia Krajowa
People charged with war crimes
People who served in civil or military structures of Nazi Germany
Deserters from the Red Army
People charged with criminal offences
The death penalty was carried out on people of fifteen different nationalities, the majority being Lithuanians and included among others Russians, Poles, Germans, Belarusians, Latvians, Ukrainians, Jews, etc.
The territory of the Tuskulėnai Manor served as a secret mass grave until 26 May 1947 when, following the order of the Presidium of the Supreme Council of the USSR, the death penalty was abolished and replaced with 25 years imprisonment at a penitentiary establishment (work camps). On 12 January 1950, the Presidium of the Supreme Council of the USSR passed a decree re-instating the death penalty.
Between October 1950 and July 1952, 182 people sentenced to death were executed at Vilnius NKGB–MGB internal prison. Their place of burial is still not known.
During the time of the Soviet occupation, the territory of the former Tuskulėnai Manor was vigilantly watched over by NKGB–MGB–KGB officials. Until the early fifties, the territory was fenced and guarded. In 1990, after the re-establishment of independence in Lithuania, the archives became accessible and witnesses could tell their stories, as a result of which the secret of this location was revealed. At the beginning of 1994, the State Security Department of the Republic of Lithuania identified a mass grave within the grounds of Tuskulėnai Manor of people sentenced to death by Soviet repressive structures. An archaeological investigation was conducted and bodies were exhumed. Forty-five graves with 724 bodies were found.
Forensic medicine experts identified that 666 victims had gunshot wounds. 506 of them were killed with one shot to the head, 111 – two shots, 31 – three shots, 13 – four shots, 4 – five shots and 1 – six shots
The skulls of 239 victims had signs of gunshot wounds and other forms of physical violence. 122 of these had marks inflicted by a blunt instrument, 112 – had signs of cuts and stabbing and 5 – had signs of deep cuts
In 2004, after the remains of the bodies exhumed were transferred to the chapel-columbarium, the place was officially opened to public on All Soul’s Day, November 2.
KGB – rus. КГБ, Комитет Государственной Безопасности – Lith. Valstybės saugumo komitetas – Committee for State Security [of the USSR]
MGB – rus. МГБ, Министерство государственной безопасности – Lith. Valstybės saugumo ministerija – Ministry of State Security [of the USSR]
NKGB – rus. НКГБ, Народный Комиссариат Государственной Безопасности – Lith. Valstybės saugumo liaudies komisariatas – People’s Commissariat for Internal Affairs [of the USSR]
RSFSR – the Russian Soviet Federal Socialist Republic
USSR – Union of Soviet Socialist Republics
Scheme of archeological research
The situation plan of the archaeological excavations of the Tuskulėnai Manor between 1994 and 1996 and in 2003. (Created by the Castle Research Centre Lithuanian Castles)
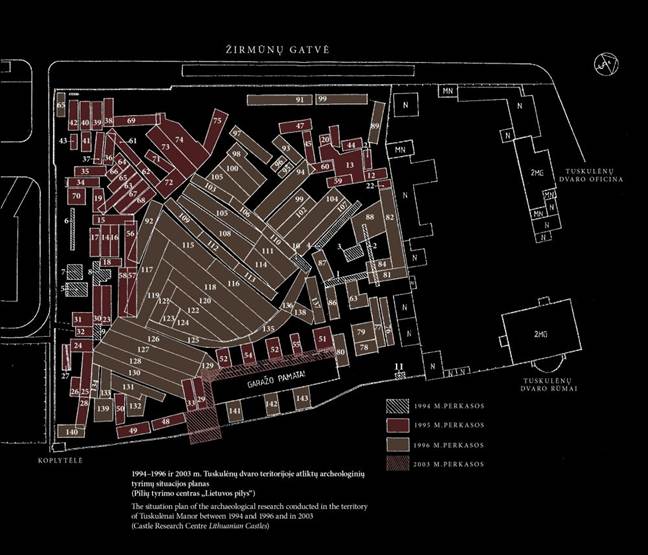
Situaition plan created by and property of Castle Research Center Lithuanian Castles. All rights reserved
Note - The Lithuanian word “PERKASOS” is TRENCHES
Look for the next article
Part 2 of 6
The “PROCESS”
EXECUTIONS BETWEEN 1944 AND 1947
Dear readers
WE NEED YOUR HELP
Dear VilNews readers, we need your help. As we have said, the victims that were executed in the NKGB–MGB internal prison in between 28 September 1944 and 16 April 1947 were buried in secret mass graves in the territory of the Tuskulėnai Manor. These victims have been found, their bodies recovered, given the dignified burial they never received and their souls have been blessed by a Holy person of the religion the worshipped.
26 May 1947, following the order of the Presidium of the Supreme Council of the USSR, the death penalty was abolished.
On 12 January 1950, the Presidium of the Supreme Council of the USSR passed a decree re-instating the death penalty. Between October 1950 and July 1952, 182 people sentenced to death were executed at Vilnius NKGB–MGB internal prison.
Their place of burial is still not known.
After July 1952 to 1961 executions continued pursuant to the 1926 Criminal Code Article 58 of RSFSR.
The burial place of these victims is still unknown.
The 1926 Criminal Code Article 58 of RSFSR was terminated in 1961 but executions continued.
The burial place of these victims is still unknown
Dear readers we would like to find where these people are buried, recover their bodies, give them the dignified burial they never received and have them blessed by a Holy person of the Religion they worshipped.
This is where we need your help. The NKVD and NKGB–MGB officers that oversaw these executions are now all dead. What ever records and documents which still exist are most likely locked away in a vault somewhere in the Russian Federation and it would seem highly unlikely that anyone in the Russian Federation would be kind enough allow access to these documents and records so that we could find out the location of the burial sites or simply tell us where these people are buried.
We know that there are people out there that know the location of some of these burial sites. Maybe it is a person that processed the documents, maybe it is some one that was just a rank and file soldier that was ordered to drive the truck that transported the bodies or was ordered to dig the trenches for the graves, maybe it is a colleague of one of these people or maybe it is the bartender that heard some of these people talk of it one night. The possibilities are endless.
Maybe none of these people with first hand knowledge of the burial sites are still alive. In that case we are sure that there are people out there with second hand or even third hand information. To have first hand knowledge of these executions would weigh very heavily on any civilized person’s heart and it is very possible that after carrying this weight inside them for many years they finally felt the need to free themselves from this burden they carried inside and told some one.
If you have any information at all, any information of any kind – Please tell us.
It is not important to us how you know, who it was, what they did or who told you.
None of this is important.
The only thing that is important is that we find where the executed people are buried.
This is all we care about.
What we want to do is best explained in the words from Bronius Eiva’s farewell letter he wrote to his wife while waiting his execution while in the prison of Ukmergės Peoples Commissariat for Internal Affairs.
“Please find out when I was shot or hanged and where they bury me.
Dig me up and take me to Šeta cemetary.”
This is all we want to do – Find where they are buried, dig them up and then give them a proper burial but we can only do this with your help.
All information will be kept strictly confidential
We are not concerned with who or what
We are only concerned with where these people are buried
If you have any information of any kind please contact:
The Memorial Complex of Tuskulenai Peace Park
Žirmūnų Gatvė 1F,
LT-09239, Vilnius
Lithuania
Telephone: +370 5 275 1223
E-mail. tuskulenai@genocid.lt
You can also contact me at vkvilnius-tuskulenai@yahoo.com
We sincerely thank you for your help.
Su pagarbe
Vincas Karnila
- Bookmark :
- Digg
- del.icio.us
- Stumbleupon
- Redit it
VilNews e-magazine is published in Vilnius, Lithuania. Editor-in-Chief: Mr. Aage Myhre. Inquires to the editors: editor@VilNews.com.
Code of Ethics: See Section 2 – about VilNews. VilNews is not responsible for content on external links/web pages.
HOW TO ADVERTISE IN VILNEWS.
All content is copyrighted © 2011. UAB ‘VilNews’.

 Click on the buttons to open and read each of VilNews' 18 sub-sections
Click on the buttons to open and read each of VilNews' 18 sub-sections 



[…] – Posted by admin “The mass graves of Tuskulėnai” Vin Karnila, Associate Editor Today: CONSEQUENCES OF THE TOTALITARIAN REGIME IN LITHUANIA 1940–1953 VIN KARNILA: It is my hope that this information we share with you will provide some insight as to […]
[…] Read more… Category : Featured red / Front page […]