
THE VOICE OF INTERNATIONAL LITHUANIA
|
VilNews has its own Google archive! Type a word in the above search box to find any article.
You can also follow us on Facebook. We have two different pages. Click to open and join.
|
The Litvaks

Watercolour by Izabele Bindler (1932 – 2003)
Jews trace their origins in Lithuania back to the days of Grand Duke Gediminas in the early 14th century, and by the late 15th century there were already thriving Jewish communities here. In time, Vilnius became known as the "Jerusalem of the North," a centre of Jewish religious learning. The Jews of Lithuania lived an intense Jewish life, and their role and influence in the major Jewish political and cultural movements were far greater than their numbers would have suggested. Vilnius became a prominent international, intellectual centre. Here there were once as many synagogues (totally 96) as churches—including the Great Synagogue, built in 1573, a vast complex of prayer spaces and schools.
Here were the innumerable yeshivas, with their famously erudite scholars (it was said that at one time there were 333 Jews of Vilnius who could recite the Talmud by heart). Here, in the 18th century, lived one of the greatest Talmudic experts of all time, the legendary Gaon of Vilna, to whom congregations from as far away as Portugal would send questions about matters of religious law or textual interpretation. Here, too, was the birthplace of the world-renowned Yiddish Scientific Institute; here was the Strashun Library, with its tens of thousands of volumes containing irreplaceable incunabula of Hebrew texts. Here flourished the most distinguished publisher of Hebrew books, the Widow & Brothers Romm, whose multi-volume Talmud, each page a masterwork of scholarship, composition, and design, was considered the pinnacle of Jewish publishing. Vilnius was also the greatest city of Diaspora learning, and at a time when others in Europe were effectively illiterate, all the Jews in Vilnius could read and write. This was so unusual that it provoked the invention of a brand-new word, "Vilner," meaning "an educated man with knowledge.
The below information about the Litvaks is from Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lithuanian_Jews
Background
Lithuanian Jews or Litvaks are Jews with roots in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania: (present-day Belarus, Lithuania, Ukraine, and the northeastern Suwałki region of Poland). The term is sometimes used, especially in Israel, to cover all Orthodox Jews who follow a "Lithuanian" (Ashkenazic and non-Hasidic) style of life and learning, whatever their ethnic background.
Lithuania was historically home to a large and influential Jewish community that was almost entirely eliminated during the Holocaust: see Holocaust in Lithuania. Before World War IIthere were over 110 synagogues and 10 yeshivas in Vilnius. Before World War II, the Lithuanian Jewish population was some 160,000, about 7% of the total population. Vilnius (then Wilno in the Second Polish Republic) had a Jewish community of nearly 100,000, about 45% of the city's total. About 4,000 Jews were counted in Lithuania during the 2005 census. There are still strong communities of Jews of Lithuanian descent around the world, especially in Israel, the United States, South Africa, Zimbabwe, and Australia.
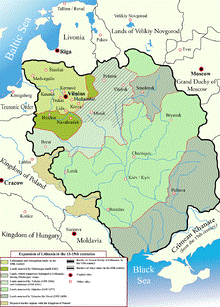
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The adjective Litvish means "Lithuanian" (Latvian Jews were known as Lettish): the noun for a Lithuanian Jew is Litvak. Of the main Yiddish dialects in Europe, the Litvishe Yiddish(Lithuanian Yiddish) dialect was spoken by Jews in Lithuania, Belarus, and in the Suwałki region of northeastern Poland.
[edit]Ethnicity, religious customs and heritage
The characteristically "Lithuanian" approach to Judaism was marked by a concentration on highly intellectual Talmud study. Lithuania became the heartland of the traditionalist opposition to Hasidism, to the extent that in popular perception "Lithuanian" and "mitnagged" became virtually interchangeable terms. However, a sizable minority of Lithuanian Jews belong(ed) to Hasidic groups, including Chabad, Slonim, Karlin (Pinsk) and Koidanov. With the spread of the Enlightenment, many Lithuanian Jews became devotees of the Haskala (Jewish Enlightenment) movement in Eastern Europe pressing for better integration into European society, and today many leading academics, scientists and philosophers are of Lithuanian Jewish descent.
The most famous Lithuanian institution of Jewish learning was Volozhin yeshiva, which was the model for most later yeshivas. "Lithuanian" yeshivas in existence today include Ponevezh,Telshe, Mir, Kelm, and Slabodka. In theoretical Talmud study, the leading Lithuanian authorities were Chaim Soloveitchik and the Brisker school; rival approaches were those of the Mir and Telshe yeshivas. In practical halakha the Lithuanians traditionally followed the Aruch HaShulchan, though today the "Lithuanian" yeshivas prefer the Mishnah Berurah, which is regarded as both more analytic and more accessible.
In the 19th century, the Orthodox Ashkenazi residents of the Holy Land were broadly speaking divided into Hasidim and Perushim, who were Lithuanian Jews influenced by the Vilna Gaon. For this reason, in modern day Israeli Haredi parlance the terms Litvak (noun) or Litvisher (adjective), or in Hebrew Litaim, are often used loosely to include any non-HasidicAshkenazi Haredi individual or institution. Another reason for this broadening of the term is the fact that many of the leading Israeli Haredi yeshivas (outside the Hasidic camp) are successor bodies to the famous yeshivot of Lithuania, though their present-day members may or may not be descended from Lithuanian Jewry. In reality, both the ethnic makeup and the religious traditions of the mitnagged communities are much more diverse.
History
Some sources claim that Jews began living in Lithuania as early as the 8th century. In 1388 they were granted a charter by Vytautas, under which they formed a class of freemen subject in all criminal cases directly to the jurisdiction of the grand duke and his official representatives, and in petty suits to the jurisdiction of local officials on an equal footing with the lesser nobles (szlachta),boyars, and other free citizens. As a result, the community prospered.
In 1495 they were expelled by Alexander Jagiellon, but allowed to return in 1503. The Lithuanian statute of 1566 placed a number of restrictions on the Jews, and imposed sumptuary laws, including the requirement that they wear distinctive clothing, including yellow caps for men and yellow kerchiefs for women.
The Khmelnytsky Uprising destroyed the existing Lithuanian Jewish institutions. Still, the Jewish population of Lithuania grew from an estimated 120,000 in 1569 to approximately 250,000 in 1792. After the 1793 Second Partition of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth Lithuanian Jews became subjects of the Russian Empire.
Lithuanian Jews in the Second World War
The Jewish Lithuanian population before World War II numbered around 220,000. During the German invasion of June 1941, 206,800 Jews were murdered by the Nazis and Lithuanian collaborators. Most of the Jews were taken into the woods to be shot in graves they were forced to dig themselves. Notable execution locations were in the Paneriai woods (see Ponary massacre) and the Ninth Fort .
Culture
Litvaks have an identifiable mode of pronouncing Hebrew and Yiddish; this is often used to determine the boundaries of Lita (area of settlement of Litvaks). Its most characteristic feature is the pronunciation of the vowel holam as [ej] (as against Sephardic [oː], Germanic [au] and Polish [oj]).
In the popular perception, Litvaks were considered to be more intellectual and stoic than their rivals, the Galitzianers, who thought of them as cold fish. They, in turn, disdained Galitzianers as irrational and uneducated. Ira Steingroot's "Yiddish Knowledge Cards" devote a card to this "Ashkenazi version of the Hatfields and McCoys." This difference is of course connected with the Hasidic/mitnagged debate, Hasidism being considered the more emotional and spontaneous form of religious expression.
The two groups differed not only in their attitudes and their pronunciation, but also in their cuisine. The Galitzianers were known for rich, heavily sweetened dishes in contrast to the plainer, more savory Litvisher versions, with the boundary known as the "Gefilte Fish Line."
Genetics
The Lithuanian Jewish population may exhibit a genetic founder effect. The utility of these variations has been the subject of debate. One variation, which is implicated in familialhypercholesterolemia, has been dated to the 14th century, corresponding to the establishment of settlements in response to the invitation extended by Vytautas the Great in 1388. A relatively high rate of early-onset idiopathic torsion dystonia in the population has also been identified as possibly stemming from the founder effect.
Jews in Lithuania today
Interest among descendants of Lithuanian Jews has spurred tourism and a renewal in research and preservation of the community's historic resources and possessions. Increasing numbers of Lithuanian Jews are interested in learning and practising the use of Yiddish.
The beginning of the 21st century was marked by conflicts between members of Chabad-Lubavitch and secular leaders. In 2005, Chief Rabbi Sholom Ber Krinsky was physically removed from the Synagogue by two men hired by the community's secular leader Mr. Alperovich, who then declared a new Chief Rabbi.
Among notable contemporary Lithuanian Jews are the brothers Emanuelis Zingeris (a member of the Lithuanian Seimas) and Markas Zingeris (writer), Arkadijus Vinokuras (actor, publicist), Gercas Žakas (football referee), Gidonas Šapiro-Bilas (pop-singer from ŽAS), Dovydas Bluvšteinas (music producer), Leonidas Donskis (philosopher, essayist), Icchokas Meras(writer), Grigorijus Kanovičius (writer), Aleksas Lemanas (singer), Rafailas Karpis (opera singer (tenor)), Šabtajus Kalmanovičius (businessman and alleged criminal mastermind), David Geringas (world-renowned cellist and conductor), Liora Grodnikaitė (opera singer (mezzo-soprano)).
- Bookmark :
- Digg
- del.icio.us
- Stumbleupon
- Redit it
VilNews e-magazine is published in Vilnius, Lithuania. Editor-in-Chief: Mr. Aage Myhre. Inquires to the editors: editor@VilNews.com.
Code of Ethics: See Section 2 – about VilNews. VilNews is not responsible for content on external links/web pages.
HOW TO ADVERTISE IN VILNEWS.
All content is copyrighted © 2011. UAB ‘VilNews’.

 Click on the buttons to open and read each of VilNews' 18 sub-sections
Click on the buttons to open and read each of VilNews' 18 sub-sections 



Great post you could have completed the following. I'm truly happy to learn to read this kind of. This can be a very informative subject matter that you're picked. keep writing.live blog
What needs to be documented is the latter day tolerance of anti antisemitism by the Lithuanian authorities. The protection of collaborators is atrocious.
*Spot on with this write-up, I truly believe this site needs considerably much more consideration. Itesting Ill probably be again to read much more, thanks for that info.
Its like you research my mind! You seem to find out so much about this, like you wrote the guide in it or something. I think which you can perform with some pics to generate the message home only a little bit, but other than that, that is great blog.
I am surprised you did not include Kaunas born Zvi Griliches, Harvard's legendary and students' beloved professor of mathematical economics/econometrics whom I used to meet at The American Economic Association conventions before he died in 1999. An educator of globally top economists and quite a number of Nobel Prize Winners in Economics (I am still puzzled why he did not receive that Prize himself!), he was one of the very first economists to scientifically/empirically demonstrate how the creation of new technology was an economic phenomenon, a very important problem for Lithuania and globally in the 21st century!
Regards,
Val Samonis
The Institute for New Economic Thinking, USA
and Royal Roads University, Canada