
THE VOICE OF INTERNATIONAL LITHUANIA
|
VilNews has its own Google archive! Type a word in the above search box to find any article.
You can also follow us on Facebook. We have two different pages. Click to open and join.
|
|
LITSHARES: |
|
A Strategy for Global Financing of Lithuania’s Development |
|
Dedicated to Those Dead or Alive Whose Blood and Brains Made Free Lithuania Possible |
|
|
|
By Valdas Samonis |
|
2/16/2012 |
|
ABSTRACT. Given the dangerous European and global economic and strategic predicaments, Lithuania (LT) needs to adopt very bold and innovative ways to “sell” to the world its extreme austerity sacrifices during the continuing period of global Great (D)Recession and its earlier periods of bold systemic transformations as well. This proposal is a new strategy to globalize LT financial-economic ties (optimal global integration) so that the nation is no longer badly cornered and unduly dependent on the moribund European Union (EU) which is distracted and disoriented by the cacophony of austerity/profligacy controversies, and actually rewarding free riders by default. By now it is rather clear that Europe alone cannot properly reward the financial virtue and sacrifice of the LT people for the sake of the future (investment) which is the most distinguishing trait of a responsible nation and a mature leadership; hence the need for LT to go before the entire “global village”. Globalization can provide huge and underappreciated benefits for a nation like LT. This litshares or litakcijos (LTS) proposal is still to be developed to a greater detail and “hands-on” policy relevance. In the first instance, LTS would appeal strongest to LT residents, diasporas, and other FOLK (Friends of Lithuania of All Kinds); then they would catch up globally rather fast. |
Introduction and Attributions
The basic insight which gave rise to my litshares (LTS) proposal for Lithuania (LT) stems from the Nobel level economist Robert J. Shiller who is the Arthur M. Okun Professor of Financial Economics at Yale University, USA, and the author of the forthcoming book entitled Finance and the Good Society (Princeton University Press) as well as the co-author (with Nobelist G. Akerlof) of my recently reviewed book Animal Spirits: How Human Psychology Drives the Economy and Why It Matters for Global Capitalism (Princeton University Press). I have gained a lot of inspiration and new understanding from my extensive discussions at The Institute for New Economic Thinking (INET), particularly interactions with the Reagan Era’s US Fed Chairman Paul Volcker and other top global experts at the INET Bretton Woods Conference in 2011. Research assistance by Ramune Samonis, University of Toronto, is gratefully acknowledged.
Right after the pinnacle of the disastrous financial crisis in 2008, The Queen Elizabeth II asked economists, “Why did no one see the credit crunch coming?” Three years later, a group of Harvard undergraduate students walked out of an introductory economics course and wrote, “Today, we are walking out of your class, Economics 101, in order to express our discontent with the bias inherent in this introductory economics course. We are deeply concerned about the way that this bias affects students, Harvard University, and our greater society.” What has happened? Rebellion from both above and below suggests that economists, who were recently at the core of power and social leadership in our society, are no longer trusted much. Not long ago, the principal theories of economics appeared to be the secular religion of society, writes Dr. Robert Johnson, Executive Director, The Institute for New Economic Thinking.
Nice Try, Europe!
Since 2007, in the five years of the continuing economic crisis, the European Union (EU) countries have been performing very badly: 22 of its 27 members incl. those from Central & Eastern Europe (CEE) have lost time as measured by several economic clocks (GDP levels, share prices, real estate values, etc). Asia has performed much more strongly but even it presents a mixed picture. In particular, the long road back for global shares as measured by the most important indices according to data by Prof. R. Shiller, The Economist, and Thompson Reuters, see Chart 1.
Chart 1: The Long & Winding Road Back to Zero for Global Shares
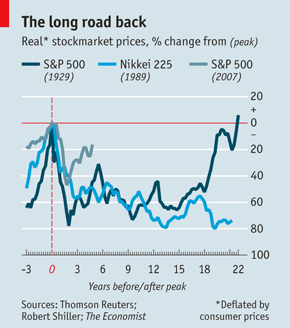
The theory of economic integration was developed over half a century ago by Jan Tinbergen, Bela Balassa, and other prominent scholars of integration. However, the house of the European integration has been built on flawed fundamentals. While the European integration fathers (Schuman, etc) were understandably in a rush to rebuild Europe on a different model as quickly as possible so it avoids the repetition of the disastrous 20th Century wars, the art and science of “architecture” in building the European integration (United States of Europe) were not properly understood and used. Simply copying the USA does not work in Europe, as we abundantly know now. With these fundamental problems, the diagnosis and prognosis for Europe does not look good at all.
With the European Central Bank/euro acting as the "new" gold standard and the current totally confused austerity/profligacy debates, Europe is probably repeating the most horrible mistakes of the bloody past. In the 1920s, after experiences of inflation and then huge and uncontrolled capital inflows, Germany lost productivity advantages in part due to uncontrolled wage growth in the environment of heavy leftist/communist propaganda. Capital inflows suddenly turned to a trickle, governments and banks were squeezed for money and credit, bank asset fire sales started, followed by runs on banks, deflation, Great Depression; the rest is history. Under the regime of the fixed exchange rates of the gold standard, this history was the logical outcome. John M, Keynes wrote in his book The Economic Consequences of the Peace back in 1919:
“Very few of us realize with conviction the intensely unusual, unstable, complicated, unreliable, temporary nature of the economic organization by which Western Europe has lived for the last half century. We assume some of the most peculiar and temporary of our late advantages as natural, permanent, and to be depended on, and we lay our plans accordingly. On this sandy and false foundation we scheme for social improvement and dress our political platforms, pursue our animosities and particular ambitions, and feel ourselves with enough margin in hand to foster, not assuage, civil conflict in the European family”.
Since 2000, the risks are even worse because of toxic assets (mortgage backed securities, other derivatives, etc) that spread around the world in and nobody knows the true financial health position of counterparties. In the near European future, we are likely to see similar credit crunch spasms, catastrophic collapses of exports/trade, and Europe's Great Depression 2: economic and political disintegration, beggar-thy-neighbor policies, conflicts, etc. The history does not repeat itself exactly though.
The USA may follow the unenviable example of Japan but at least that is a slow and gradual decline that gives opportunities for new bursts of the US "animal spirits" and new turnarounds, e.g. via increased immigration, new and exports-oriented manufacturing technologies, etc.
Without getting here into undue larger debates, it is sufficient to sum up that conventional European approaches fail to provide remedies to the great majority of the economic Greek Tragedies that afflicted the continent and the world, incl. the current Great (D)Recession; this rather sweeping assertion is not even controversial in early 2012. The reason it is so is that these standard economic theory approaches completely fail to account for the operation of “animal spirits”, a concept dating back to John M. Keynes. Animal spirits are our interpretations of finance, economics and the economy, our mental/psychological forces and constructs, spiritus animalis from the original Latin. They include: (non)confidence (with its Keynesian style multipliers), the issue of fairness in wage determination and other areas (like comparative pensions among nations), corruption and bad faith phenomena in the societies, money illusion that people usually operate under, and stories that are our practical and simplified ways of thinking about our economic and financial affairs.
Enter the Center: Lithuania
Located at the geographical center of Europe, Lithuania has been leading the postcommunist world in economic and political reforms, shedding development retarding legacies of the occupying power (USSR), and trying to re-join the global village after some half a century of the Soviet occupation and the resultant destruction of ties to the world. Since 1990 Declaration of Independence, LT has gained a unique global recognition, even admiration, for its valiant and peaceful freedom-seeking anticommunist revolution and thus amassed a lot of global political capital and global good will. In the interwar independence period that included the global Great Depression, LT had a second strongest currency in Europe, after the Swiss franc. The problem is that LT remains a very timid seller of its stamina, achievements, etc, seemingly resigned to sacrifices without getting much credit for them in this global village of ours.
Since the Annus Mirabilis 1989, the theory was that Central and Eastern Europe (CEE) would use its abundant and (relatively) educated labor force to grow faster and on a more sustainable and consumer-oriented (prosperity) basis due to a decisive shift to markets and European integration. The EU integration was supposed to anchor market reform achievements and help secure new sustainable growth as outlined in the now almost forgotten EU Growth and Stability Pact.
What got in the way is the theory of (rational?) expectations?
True, CEE did receive a sort of a very modest version of Marshall Plan from the EU. True to four EU freedoms, Western Europe has been opening in fits and starts to labor movements (emigration) from CEE. So when new CEE policymakers were implementing pretty liberal market reforms, they should have anticipated some outflows of labor force to much higher bidders in Western Europe due to simple demonstration effect. Poorly understood legacies of communism are at fault here.
What got in the way is the law of unintended consequences in complex processes?
When the British opened their labor markets to the East, they anticipated some 10-12 thousand immigrants from Poland, for example, what they got is some one million and rising. Who knows what the figure will be a longer time after Germany’s opening in 2011?
What got in the way is the paradigm of hard-to-calculate policy externalities?
The current Prime Minister Andrius Kubilius Government of Lithuania adopted a very ambitious (no IMF help even sought!) and a rather very harsh austerity modeled on the reigning traditional EU thinking in order to clean the Augean stable of Lithuania’s finance wrecked by the former Soviet nomenklatura hijacked governments that largely used “easy” EU money to place their cronies in plum jobs in LT and Brussels (to the exclusion of younger generation of course), “prikhvatize” real estate and keep it from any socially beneficial taxation, etc. The Kubilius Government’s harsh austerity policies (the so called internal devaluation) cutting public sector wages, social expenditures (by about one third) and increasing some taxes, etc, in a national fiscal belt tightening (“diet”) that has probably been the steepest in recent memory globally. Predictably, the GDP collapse was horrible at some 20%. The LT people have been pretty much resigned to the fate, in a stark contrast to Greece.
The Kubilius Government has been operating under the handicap of the currency board (CB) arrangement which is an alternative monetary arrangement to a central bank and a national monetary policy, e.g. using short-term interest rates. Against a better advice, CB was introduced as far back as 1994, even though LT has had very good interwar comparative experiences with running the second strongest currency of Europe in a classical central bank formula that fits the responsible nation like LT very well. As opposed to the classical central bank, CB allowed no room for monetary easing while doing harsh austerity. For all practical reasons, LT currency has been hard pegged to euro resulting in a quasi Eurozone membership of LT. The formal LT membership of the Eurozone was denied by Brussels on the flimsy grounds of miniscule short-term inflation targeting problems, while France and other Eurozone core countries have been rather openly violating the EU’s fundamental Maastricht Treaty and the Growth and Stability Pact. As we know from the world history (e.g. Argentina), CB regimes can be very destabilizing (incl. runs on banks, etc) during the kind of deep turmoil periods that Europe is experiencing since 2008.
Despite repeatedly proving the nation’s responsibility and sacrifice (investment) capabilities via austerity, etc, LT did not attract much European/Western direct investment so the productivity remained at low postcommunist levels at the time when emerging Asia provides a stiff global competition.
Thus, very unlikely EU countries, like the Soviet communist exploited and impoverished Lithuania, have long showed the way to Europe by adopting serious austerity policies that go almost to the point of "eating the dog food", to use a hyperbole. Unfortunately, this good model that Europe has been looking so desperately for (and could not find) is drowned in the cacophony of bureaucratic quarrels around bailing out Greece and other profligate countries that are, so far at least, the true winners in Europe. Theoretically, if the nation like LT adopts a conventional, hard austerity policy, a serious “diet” designed to improve public finances and the resultant “crowding out effect”, the nation should get into the global position of substantially improved financial reputation, presumably also the much lower cost of its longer-term capital.
However, it all comes to empirics and experiential learning. Theoretically, you can think of a hypothetic success story of "expansionary austerity". It would be due to the removal or reduction of the crowding out effect (COE) that government profligacy usually causes. The removal of COE should theoretically lead to productivity increases on the strength of the argument that business can innovate/do business better than government does; vide long economic history of postcommunist countries and of the world in general. However, the problem is the time horizon. If austerity leads to the catastrophic collapse of GDP, then emigration of hard-to-replace human resources and capital flight usually follow. In short, austerity can work in the long run provided that the long run exists at all; that is if the economy is not dead by that time, to paraphrase Keynes. Ultimately, economic policy is about experiential learning, empirics that are. When a nation’s economy contracts, as LT did by some 20%, and its debt continues to grow, a big problem develops for the taxpayers. This is why Europe is in turmoil right now. “Expansionary austerity” is an oxymoron, every bit as it sounds, in the mid-term at the very least.
Before they realized what is going on and who was robbing them, the Lithuanian people got clabbered by this new ambitious austerity policy and the younger ones started emigrating in catastrophic numbers, seeing no future in the country whose GDP was reduced (from a low post-Soviet level) by some 20% by the combination of the old nomenklatura rent-seeking policies and the continued global Great Recession. Lithuania is hollowing out, unfortunately.
While the Lithuanians made huge sacrifices and so “invested” in the future, the Greeks have been continuing the party here and now until the last bottle or perhaps they can get another one, and another:).
In the current state of European affairs, Greeks won, Lithuanians lost! This is the tale of two integrating nations: they are even related since ancient times according to a Greek Palemonas legend.
Litshares: The Conceptual-Analytical Framework for Globalizing Lithuania
Despite some serious problems with the first stage of globalization, it can provide huge and so far very poorly understood benefits for a responsible, thousand-year nation like LT. How about developing an innovative strategy to get some hard earned respect and actual long-term financial capital for sustainable development of LT from the global markets? Below is my proposed case for litshares or litakcijos (LTS) for LT.
Writing in the Harvard Business Review (HBR, January-February 2012), Prof. Robert Shiller suggested a simplifying assumption that a nation can be treated as a corporation from an investment and developmental point of view. Corporations use both debt and equity to finance their investments and operations; nations use only debt.
The logic goes that nations like LT should replace much of their existing national debt with shares in the “earnings” of their economies. This would allow them to better manage their financial obligations, present themselves better before global markets, and could help prevent future financial crises. It might even lower a nation’s borrowing costs in the longer run. LT paid something like 10% as a cost of capital in the recent past, usury really.
National shares would function much like corporate shares traded on stock exchanges of the world: London, Frankfurt, NYC, Hong Kong, Toronto, etc in the case of LTS. They would pay dividends regularly. Ideally, they would be in perpetuity, although a nation could always buy its shares back on the open market. The price of a share would fluctuate from day to day as new knowledge about a nation’s economy came out and have been digested by global analysts. The opportunity to participate in the uncertain economic growth of the new issuer nation (esp. “hidden gem” like LT) might excite investors, just as it does in the stock markets around the world.
Helped by Dr. Mark Kamstra, Prof. Shiller developed some insights on how these new national shares could work. In my proposed case of LT, these litshares (LTS) could pay a quarterly dividend equal to exactly one-billionth of the nation’s quarterly GDP (some 30 billion LTL in Q4, 2011), the simplest measure of national earnings. The fractional value of LTS could be different of course; but the important consideration in case of LT is to attract all the global investors, even smaller ones. The payoff would vary of course, depending on how well the nation like LT does, what the GDP growth is (over 100 billion LTL in 2011). If the economy surprised the investors on the upside, dividends would go up; if it declined, dividends would fall. The global markets would determine the price of an LTS which would be normally volatile. It would depend not only on the most recent dividend but also on the investors’ expectations for the future, which can change for the better precisely because of austerity “investments” by LT or any other nation, as opposed to profligacy of other nations, etc. There is s some evidence that a LTS might often be expensive relative to the dividend, which would be good for the national issuer. Prof. Shiller observes that shares of many US corporations and 10-year US Treasury notes sell for over 50 times their annual dividend. Since the growth rate of the real US GDP has been higher than that of real S&P 500 earnings in the past (3.1% annual GDP growth versus 2.5% annual S&P 500 growth over the past half century), such shares might sell for a multiple higher than 50.
Litshares Could Be Attractive Investments Globally
The advantage of keeping LTS equal to a billionth part of the economy is that people will know exactly what they are getting: one-billionth of a thousand-year old nation like LT is real and easy to understand for global investors. Such shares based on GDP have the great merit of being really clear, simple, and understandable to investors globally. Other measures of national earnings might seem to some analysts more appropriate than GDP but would sacrifice the great virtue of simplicity, clarity, transparency. This kind of simplicity and clarity encourages the development of badly needed confidence and trust that governments will not shirk their obligations at any time in the future. This is much better confidence and trust building strategy than any heavily advertised “magic” mechanisms like currency board that LT adopted against a better advice back in 1994.
LTS may appeal to international investors even more than corporate shares do because LTS would avoid the problem of the so called moral hazard. Here is the reason that Prof. Shiller stresses. If international investors ever acquired a good fraction of a nation’s corporate shares, the nation would have an incentive to raise the corporate profit tax on those shares or regulate them to reduce their value. If a nation did so, like the Kubilius Government rather erroneously did in LT, it would benefit without technically violating any promises. The issuance of LTS, however, would involve a strong and easily understandable promise of share in the value added (GDP) to global investors. If the shares paid dividends in the nation’s domestic currency like LTL, it would eliminate another moral hazard associated with the traditional debt. If the national shares strategy is adopted, the nation could not reduce its real obligations by creating inflation (e.g. via devaluation, as is already happening in some CEE countries), as they can with conventional government debt, because their nominal GDP would increase in proportion to the inflation thus created.
Speaking of Greece, Prof. Shiller asks what effect could national shares have had during the Great Recession and its aftermath? Greece’s real GDP fell 7.4% in 2010. If its shares were leveraged substantially, e.g. five to one, then the dividend paid on them would have fallen by about 40%. This would have done much to alleviate the crisis, making it easier for notoriously rebellious Greek taxpayers to bear. It would have given Greece a bailout without any scandal-ridden international controversies, loss of face and reputation or broken promises. After the fact, investors in Greek national shares would have been unhappy. But they still might have been willing to buy them, considering the very possible upside of such a leveraged investment. Global investors eagerly buy leveraged corporate stocks, so it is plausible that they would buy leveraged national shares as well. Global markets for national shares would fundamentally change the economic atmosphere (and confidence) in a nation like Greece or LT. An immediate market response would accompany every new governmental plan (strategy) affecting the future of the economy and society, generating discussions, free publicity, and a broader knowledge of each nation’s development plans, as well as much more energetic flows of global resources towards nations with plans that passed the transparent global markets test. This is much simpler and easier to understand for investors than the obscure and at times obviously disreputable work of traditional credit rating agencies or corrupt analysts.
In Lieu of Conclusions
With national share prices going up and down, LTS or other such shares might look to some analysts as an unwelcome extension of financial capitalism. Financial industry is in deep disrepute globally for causing this Great (D)Recession. But, in fact, the thoughtful implementation of disciplined financial capitalism has been the story of every successful nation in history. LT has made a very good headway. We should have real global markets for nations like LT; such “macro” markets would track their successes much more accurately and justly than stock markets usually do. And LTS would do the necessary justice to serious efforts and results of structural reforms and financial discipline like in LT. Stock markets trade only in claims on corporate earnings after corporate taxes, which is an unreliable measure of a nation’s success. We can do better, concludes Prof. Robert J. Shiller who was among the very few experts to have predicted this Global (D)Recession. He argues that, rather than condemning finance, we need to reclaim it for the common good. He makes a powerful case for recognizing that finance is one of the most powerful tools we have for solving our common problems as mankind, and increasing the general well-being of people. We need more financial innovation and more globalization that would be developed in the policy environment of proper risk and knowledge management. The acute need for modern risk/knowledge management arises because global markets do an excellent job of nurturing financial innovations that people want (rather than need); but they are much less useful for planning for when things go wrong, like in this Global (D)Recession.
With regard to my LTS proposal, in the first instance, LTS would appeal strongest to LT residents, diasporas, and other FOLK (Friends of Lithuania of All Kinds); then they would catch up globally rather fast. My LTS proposal is to be developed to a much greater detail and “hands-on” policy relevance.
Valdas Samonis
INET and SEMI Online
Toronto-New York City-Vilnius
For more on V. Samonis publications, please consult:
V. Samonis Author Page on Amazon.com
http://www.amazon.com/Valdas-Samonis/e/B0031SF300/ref=ntt_dp_epwbk_0
and/or search for the name Samonis (Val or Valdas) in Google.com.

- Bookmark :
- Digg
- del.icio.us
- Stumbleupon
- Redit it
VilNews e-magazine is published in Vilnius, Lithuania. Editor-in-Chief: Mr. Aage Myhre. Inquires to the editors: editor@VilNews.com.
Code of Ethics: See Section 2 – about VilNews. VilNews is not responsible for content on external links/web pages.
HOW TO ADVERTISE IN VILNEWS.
All content is copyrighted © 2011. UAB ‘VilNews’.

 Click on the buttons to open and read each of VilNews' 18 sub-sections
Click on the buttons to open and read each of VilNews' 18 sub-sections 



A good read! With powers united, we could really see a powerful renaissance of Lithuania. No one should ever underestimate the hearts and stamina of Lithuanian people.
Lietuva jums(buvusiam lietuviui) dekoja uz pasakima jog jus buves! Lietuva klestes tik duokim Jai laiko isleisti visus buvusius
' lietuvius"
Interesting question!
But with my LitShares(SM) financial strategy and my broader national economic strategy that I proposed long ago, we could see the powerful renaissance of LT, a thousand year old nation that has been in much worse predicaments over that 1000 years!
Aciu labai uz gera komentara! Valdas
What kind of freak can buy shares country that will disappear in next 50-80-100 years.
[…] Read more… Category : Featured black / Front page […]