THE VOICE OF INTERNATIONAL LITHUANIA
|
VilNews has its own Google archive! Type a word in the above search box to find any article.
You can also follow us on Facebook. We have two different pages. Click to open and join.
|
 |
Commemorating January 1991
|

21 January 1991: Soviet military vehicles dominated the streets of Vilnius. Dag Andersen and I presented a letter from Oslo Municipality, signed by Mayor Michael Tetzschner. Oslo offered Vilnius to become its first friendship city in the West. The letter was enthusiastically received by the Vilnius Mayor Arunas Grumadas and Deputy Mayor Regimantas Ciupaila.
Photo: Aftenposten, Norway.
Aage Myhre, VilNews Editor-in-Chief
aage.myhre@VilNews.com
We were two Norwegians working very much with Lithuanian affairs during autumn/winter of 1990-91, Dag Andersen and me. During our visit to Vilnius in January 1991, we showed our respect to President Vytautas Landsbergis in his Parliament office and worked with journalists to spread the message about the Soviet assault to the world.
We also brought with us a letter from the City Council Leader of Oslo, Michael Tetzschner inviting the Mayor of Vilnius to sign a sister city agreement. We handed the letter over to Mayor Arunas Grumadas on 21 January while Soviet troops were standing around in the streets and armoured vehicles roared around us.
The twin city agreement was signed a few months later, and Oslo became thus the first Western city to enter into such an agreement with Vilnius. I saw it as an important symbol of friendship and solidarity at a difficult time for a country under tremendous pressure and terrible abuse from Lithuania’s power loving neighbour to the east.
We came via Riga
We were a small group of Norwegians who travelled from Oslo to Vilnius a few days after the infamous Soviet attack and its killings on the 13th of January 1991. It was originally planned as a larger delegation, with parliamentarians, but they had to postpone their trip due to the death of our Norwegian King Olav.
We came to Vilnius via Copenhagen and Riga, whereto Scandinavian Airlines as the first western airline had established a route a few months earlier. Travel insurance cover was 400% higher than normal. The Baltic States were now defined as a war zone.
In Riga we first visited the Radio and Television House. The smoke from the many bonfires around the building lay like a blanket over the area, with a penetrating but good smell of firewood. It was an impressive sight to see the thousands of Latvians who camped around the territory in tents and primitive shelters to protect the freedom of peaceful broadcast against the Soviet perpetrators.

We, our Norwegian team, together with journalists travelled to Latvia and Lithuania as soon as we could after the Soviet attack in January 1991. The Balts refused to accept the Soviet invasion. They did their utmost to protect their governments and media. Here we are with 'activists' in Riga. For several weeks they made bonfires, staying here in tents night after night to demonstrate against the new Soviet assault.
Photo: Aage Myhre, January 1991.
- Bookmark :
- Digg
- del.icio.us
- Stumbleupon
- Redit it

Visit to the Lithuanian
Parliament (Seimas)
22 years later

Lithuanian Foreign Ministry issued primitive passes for us,
and we managed to get through a long maze of controls,
barbed wire, concrete blocks and barricades that surrounded
the Lithuanian Parliament those January days in 1991. We got
the opportunity to visit this brave Parliament President,
Professor Vytautas Landsbergis, in his office. Here he
lived day and night for weeks while the Soviets
surrounded the building with troops and tanks.
Text and photos: Aage Myhre, Editor-in-Chief
aage.myhre@VilNews.com
This year I marked 13 January in the Lithuanian Parliament Building, 22 years after I in 1991 stood here in this building, along with Professor Landsbergis and looked out the window at the bonfires, barricades and the huge crowd of unarmed people who had gathered to protect their president and the country's future as a free nation.
I came here today with a group of young Lithuanians, most of them so young that they do not have their own memories of what happened here 22 years ago. Yet the memories of the sad events in January 1991 are very much alive and present for them. They want to remember that freedom and independence is not something you can take for granted, and they want to pursue a political career. They are Lithuania's future politicians. They are the future of young, well-educated, smart leaders that this country a few years ago could only dream about.
I walked around with them in the Parliament this 13th January. I saw their interests, and their pride in belonging to a great nation like this.
I also saw large photographs on the walls, with Lithuania's parliamentary history of the interwar time and from the years after the Declaration of Independence 11 March 1990. The sadness I felt when I walked around in these corridors 22 years was gone, now I felt only joy, and optimism regarding the country's future and its political leaders for the years to soon come.

Entrance to the old part of the Parliament.
- Bookmark :
- Digg
- del.icio.us
- Stumbleupon
- Redit it
 The bonfires and
The bonfires and
barricades that
saved Lithuania


In January 1991, the Lithuanian Parliament was for weeks surrounded by hordes of people, bonfires, concrete blocks and vehicles that the Lithuanian people had brought there to protect their leader and their elected representatives against the Soviet atrocities against innocent
people. Today, exactly 22 years later, the Parliament is
surrounded by peaceful, quiet winter streets.
Top photo: Zenono Nekrošiaus
Text and photos: Aage Myhre, Editor-in-Chief
aage.myhre@VilNews.com
It was not bonfires, concrete blocks, steel beams, barbed wire or tractors which in themselves rescued Lithuania in January 1991. But it was these simple remedies, not weapons, that came to represent the peaceful resistance Lithuanians showed towards their powerful opponent from the east.
I'll never forget the sight of the flames and the large crowd that met me the day I was walking down the Gedimino prospekto towards the Parliament an icy winter day in January 1991. I read a combination of hope and despair in the faces, but first of all I saw determination. This time we will not surrender! The Soviet Union shall not again be allowed to trample us down under its iron heel!
The tactics succeeded. The Lithuanian people united as never before, or since, and the assailants had to withdraw in favour of a free and democratic Lithuania. Some of the symbols of this defining moment in our country's history can still be seen outside the Parliament.


In January 1991 I crossed the barricades to visit President Vytautas Landsbergis in his Lithuanian Parliament office, while the Soviet troops and tanks continued to surround the building. 14 years later we visited together what was left of the concrete barricades from that time. These are now protected by a glass structure.

1991

2013


1991


2013

It was very touching to see how the Balts acted to keep their newfound freedom and protect their home country during the very difficult January days of 1991. Here, at the entrance to the Lithuanian Foreign Ministry, the young men have put on homemade clothes that are meant to look like uniforms. They carry rifles and other weapons they have found in their homes. Sand bags have an important symbolic effect. Brave guys!
Photo: Aage Myhre, 18 January 1991.
- Bookmark :
- Digg
- del.icio.us
- Stumbleupon
- Redit it
By: Linas Johansonas LTnews.net
(Cleveland) Linas Muliolis was your average young Lithuanian born in the USA. The son of World War II refugees, Linas grew up in Cleveland's Lithuanian community. In January 1991, he was just a month away from turning 21 years old & was in Vilnius during the historic Jan. 13 events. Earlier this week, LTnews.net talked with Linas about his experiences 22 years ago.
HOW DID A YOUNG MAN FROM CLEVELAND END UP IN VILNIUS DURING A 'REVOLUTION'? "I went there (Lithuania) to live for a year, to study language at Vilnius University. Things were heating up and in the beginning of January, I went there (parliament building) and volunteered to be an interpreter. I worked in the information bureau with Rita Dapkute".
WERE YOU AT THE PARLIAMENT BUILDING ON JAN. 13? "Yes. I was there for four days with only two, four-hour breaks of sleep ..... Had my own gasmask issued to me". (it was 108 hours with 2 four-hour naps)
- Bookmark :
- Digg
- del.icio.us
- Stumbleupon
- Redit it
If there were those in the West who had not heard of Lithuania before, they almost certainly had by the end of the day 13 January 1991

Heavy tanks were used by the Soviet forces when they attacked the Vilnius TV tower and the Parliament building on 13 January 1991. They were met by a wall of unarmed people who refused to allow the intruders to again take control of their homeland.
Text: Aage Myhre, editor-in-chief
aage.myhre@VilNews.com
"Lithuanians, do not resist, your government has betrayed you. Go home to your families and children."
This was the repeated announcement from the Soviet military vehicles with loudspeakers on the roofs, so-called sound trucks that rolled through the streets of Vilnius in January 1991. But fortunately for Lithuania and the United Europe that we now take more or less for granted, there was a music professor and a complete small nation that wanted it all differently.
Had it not been for this peaceful struggle of recovered freedom against an invasion and occupation, the people of the Baltic States never wanted or agreed to, the map of Europe would most likely have looked quite different today.
If there were those in the West who had not heard of Lithuania before, they almost certainly had by the end of the day 13 January 1991. It was the day that Soviet troops struck in Vilnius. The bloodshed that followed made headlines around the world. The attack was apparently an attempt to stop the Lithuanian independence movement in its very beginning.
When the smoke of the Soviet weapons ceased, more than a dozen people had been killed, hundreds injured. Soviet’s attack, and especially the killings at the TV tower, brought not only fame and sympathy for Lithuania from around the world, it was also a defining moment for the Lithuanians themselves.
The bloodshed meant that a point of no return had been crossed. If there was someone who until now had believed that a peaceful settlement with Moscow was possible, it was now clear to everyone that such a thing was unthinkable.
VIDEO FROM 13 JANUARY 1991
The 1991 January events took place in Lithuania between January 11 and 13, in the aftermath of the Act of the re-establishment of the State of Lithuania. As a result of Soviet military actions, 14 civilians were killed and more than 1000 injured. The events were centered in Vilnius, along with related actions in the cities of Alytus, Šiauliai, Varėna, and Kaunas.
- Bookmark :
- Digg
- del.icio.us
- Stumbleupon
- Redit it
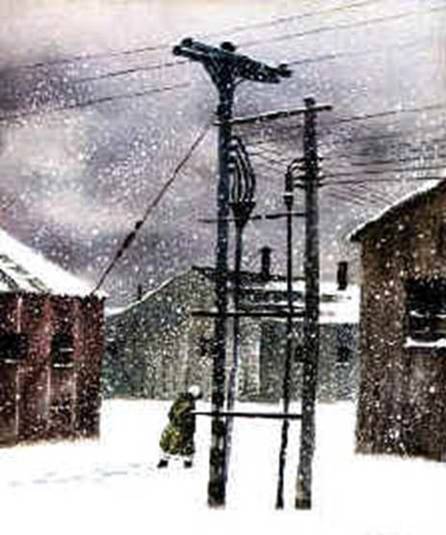
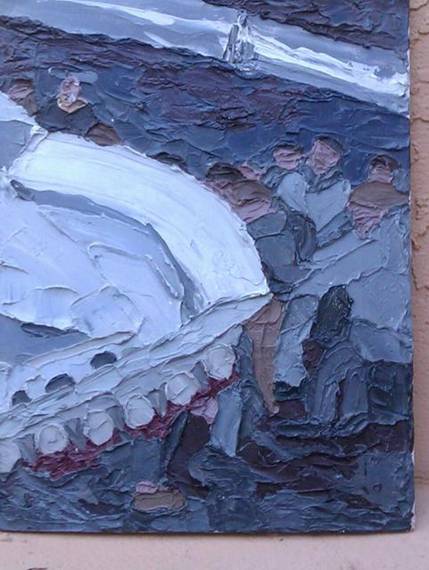
13 January 1991
through an artist’s eyes
 The photo. |
Artist Ruta Brazis-Velasco: This painting was done as an exercise in college of a trauma painting, done in oil with a pallet knife in 5 minutes. I used a Magazine type book that documented the truth.” |

- Bookmark :
- Digg
- del.icio.us
- Stumbleupon
- Redit it

2nd World War was over
- though not in Lithuania
Christmas of 1945 was over most of the world celebrated with a joy and delight almost never before seen. Young and old gathered in homes, on streets and in churches. An endless series of victory ceremonies took place in almost every corner of the world. With a deep sense of joy and gratitude all wanted each other warm, comfortable and relaxing Christmas holidays, knowing that the Nazi era was over and that the world now more than ever could look forward to a future of peace and prosperity. The war had finally released the grip, forgotten was the economic recession of the 1930s. Forgotten was also our Western World’s close friends and neighbours - the Baltic States.
On a small farm in northern Lithuania, in the outskirts of the village Šilagalis, Christmas 1945 is nearing. It is the 22nd of December, and the mother of the house feels very happy that her 21 year old son Povilas has finally come home to visit after having been away for many months.
He has come to change into dry clothes to keep him warm through the cold winter days waiting. His mother is infinitely happy to have her son home this one day, and she does everything she can to treat him with all the good food and drink their little farm can produce. You never know how long it will be till next time.
Povilas had joined a local partisan group earlier in 1945, and now spends all time in the North Lithuanian forests where the local "forest brothers" have established their hideouts. It is from these caches, usually at night, that they conduct their operations against military installations and forces of the Soviet Red Army and NKVD (the secret Soviet police that later changed name to KGB).
- Bookmark :
- Digg
- del.icio.us
- Stumbleupon
- Redit it

Joseph Stalin (1878 – 1953) One of the most powerful and murderous dictators in history, Stalin was the supreme ruler of the Soviet Union for a quarter of a century. His regime of terror caused the death and suffering of tens of millions, but he also oversaw the war machine that played a key role in the defeat of Nazism.
Illustration: http://sspurlock.wordpress.com
By Tony Olsson, North Devon, UK (guest blogger)
How could the western nations ignore the abuse by its wartime ally the USSR of all of the countries it had conquered during WW2?
Why didn’t America and Britain declare war on the USSR as its tanks and troops invaded Hungary, Czechoslovakia, and Poland?
- Bookmark :
- Digg
- del.icio.us
- Stumbleupon
- Redit it
The longest and bloodiest
partisan war in modern Europe
LITHUANIA, LATVIA & ESTONIA 1944 – 1953
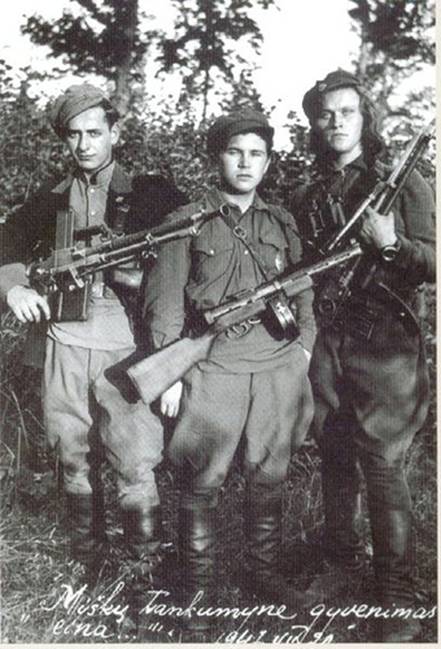

Lithuanian ‘forest brothers’ from the so-called "Vytis" military district.
Text: Aage Myhre, VilNews Editor-in-Chief
Tell a Lithuanian that his country was liberated and peace after WWII was restored on the 9th of May 1945, as the Russians claim. Tell him that this 2011 May it is 66 years since the Soviet Union and the Western world defeated Hitler's Nazi regime, and that Lithuania since then has been a free, happy country in line with what other European countries experienced after they were occupied in 1939 – 1940 and liberated in 1945. Do not be surprised if you get an angry and annoyed look back. For while we in the Western world, in Russia and in other parts of the world joyfully could celebrate the liberation and the recovered freedom after the World War, Lithuania, the other two Baltic states, and Ukraine were forced to realize that one war had been replaced by a new, much bloodier and more protracted war, lasting from 1944 to at least 1953. What we in the west celebrated in May 1945 was by Lithuanians and the other occupied countries experienced only in 1990 –1991.
- Bookmark :
- Digg
- del.icio.us
- Stumbleupon
- Redit it
CHRISTMAS IN SIBERIA
A Lithuanian family at Lena river, 1942
“The tents were freezing cold, harsh, and distressing; so, the adults decided to build better living conditions. "We can build barracks," said one Lithuanian, "We can catch the logs in the Lena River." The men waded barefoot into the icy water, caught floating logs, brought them to shore, and built the barracks. They covered the outside walls with snow and ice which they learned would help keep out the frigid temperature. They also found a large iron stove, which they placed in the middle of the building.”
- Bookmark :
- Digg
- del.icio.us
- Stumbleupon
- Redit it
A tribute to those who survived Siberia
- Bookmark :
- Digg
- del.icio.us
- Stumbleupon
- Redit it
This train engine towed cattle cars filled with thousands of innocent deportees to Siberia

A Monument to the Empire, silver bromide print by Juozas Kazlauskas, 1989 (copyright Dalia Kazlauskiene). This train engine towed cattle cars filled with thousands of innocent deportees from Lithuania, and other Eastern European countries, until 1953, when Stalin died. Kazlauskas was one of the first people to visit deportation sites and photo-document them. When he started exhibiting these images, the Soviet (later Russian) government, out of embarrassment, cleaned many of these sites up, so they no longer exist. Nevertheless, these governments never brought anyone to account for the 20 million genocidal murders that were committed by Stalin and his henchmen.
Courtesy: Val Samonis
- Bookmark :
- Digg
- del.icio.us
- Stumbleupon
- Redit it
My great grandfather came home
from Siberia in a suitcase

The farm where my wife’s great-grandfather lived
before the deportation to Siberia.
By Aage Myhre, Editor-in-Chief
Egle, my wife, comes into my study here in Vilnius as I am preparing the articles about the deportations to Siberia. "You should tell the story of my great-grandfather," she says. Because she, like almost all other families in Lithuania had relatives who were sent to Siberia. Many never returned, as was the case with her great-grandfather.
- Bookmark :
- Digg
- del.icio.us
- Stumbleupon
- Redit it
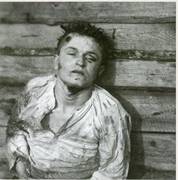
“The mass graves of Tuskulėnai”
A series of articles in 6 parts
By Vincas Karnila, Associate editor
vin.karnila@VilNews.com
 |
INTRODUCTION |
 |
Part 1 of 6 |
 |
Part 2 of 6 |
 |
Part 3 of 6 |
 |
Part 4 of 6 |
 |
Part 5 of 6 |
 |
Part 6 of 6 |
 |
THE SUMMARY |
- Bookmark :
- Digg
- del.icio.us
- Stumbleupon
- Redit it
776 years since the Sun
Battle in North Lithuania
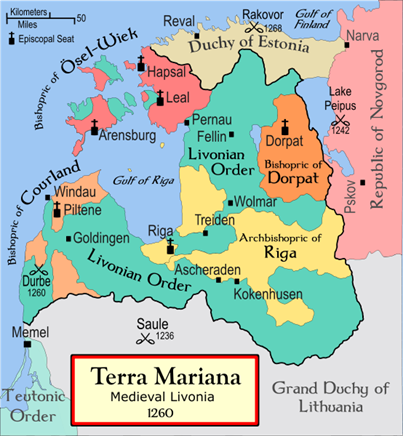
The Livonian Confederation in 1260, showing where the Battle of Saule
(battle of the sun) took place, near today’s Šiauliai in Northern Lithuania.
The Battle of Saule (German: Schlacht von Schaulen; Latvian: Saules kauja; Lithuanian: Saulės mūšis or Šiaulių mūšis) was fought on September 22, 1236 between the Livonian Brothers of the Sword and pagan Samogitians. Between 48 and 60 knights were killed, including the Livonian Master, Volkwin. It was the earliest large-scale defeat suffered by the orders in Baltic lands. The Sword-Brothers, the first Catholic military order established in the Baltic lands, was soundly defeated and its remnants accepted incorporation into the Teutonic Order in 1237.
- Bookmark :
- Digg
- del.icio.us
- Stumbleupon
- Redit it
The trampling of
Lithuania’s history
Many Lithuanian historians continually choose not to understand, appreciate, and respect the impact and grandeur of Lithuanian history
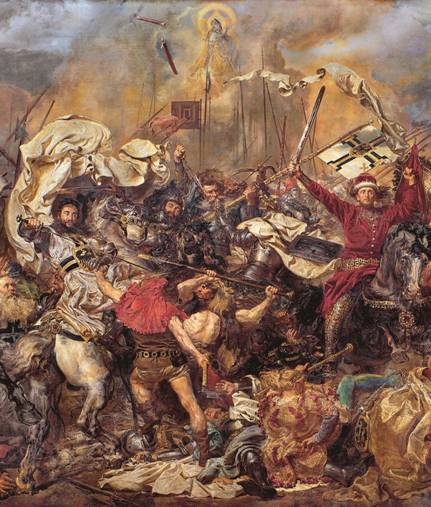

Žalgirio Mūšis (Battle of Tannenberg or Grunwald), fought on 15 July 1410, during the Polish–Lithuanian–Teutonic War, was the most significant, largest, and fiercest battle in medieval European history. It was Lithuania’s Vytautas the Great, the ultimate warrior king, whose strategic and tactical genius ensured victory for Lithuania and its allies.
Detail from a painting by Jan Matejko (1878).
By: Jon Platakis
Over 200 years of foreign occupations left our history suppressed, maligned, and if not stolen outright, then at least borrowed by our neighbors. One browses the internet, or leafs through history books and journals about Lithuania, and immediately notices our great Lithuanian names russianized or polonized; Lithuanian historical events are distorted in many versions, such as, Žalgirio Mūšis (Battle of Tannenberg or Grunwald) where descriptions of Vytautas’ participation is minimized or almost non-existent. It was mostly Lithuanian blood that was shed in this most significant, largest, and fiercest battle in medieval European history. It was Vytautas, the ultimate warrior king, whose strategic and tactical genius ensured victory for Lithuania and its allies (Sven Ekdahl, “The Turning Point in the Battle of Tannenberg-Grunwald/Žalgirio-1410.“ Lithuanian Quarterly Journal of Arts and Sciences, Volume 56, No.2-Summer 2010). This list can go on and on.
- Bookmark :
- Digg
- del.icio.us
- Stumbleupon
- Redit it
VilNews e-magazine is published in Vilnius, Lithuania. Editor-in-Chief: Mr. Aage Myhre. Inquires to the editors: editor@VilNews.com.
Code of Ethics: See Section 2 – about VilNews. VilNews is not responsible for content on external links/web pages.
HOW TO ADVERTISE IN VILNEWS.
All content is copyrighted © 2011. UAB ‘VilNews’.

 Click on the buttons to open and read each of VilNews' 18 sub-sections
Click on the buttons to open and read each of VilNews' 18 sub-sections