THE VOICE OF INTERNATIONAL LITHUANIA
|
VilNews has its own Google archive! Type a word in the above search box to find any article.
You can also follow us on Facebook. We have two different pages. Click to open and join.
|
Author Archive
- Posted by - (0) Comment
Independent Lithuania
(1918–1940)

After Vilnius was occupied by the Russian Bolsheviks in 1919, the government of the Republic of Lithuania established its main base in Kaunas. Later, when the capital Vilnius was forcibly annexed by Poland, Kaunas became the temporary capital of Lithuania,a position it held until 28 October 1939, when the Red Army handed Vilnius back to Lithuania. Here a picture from the Presidential Palace of the Republic of Lithuania in Kaunas, around 1930
At the end of World War I the Germans allowed the Vilnius Conference (18–22 September 1917) to convene (elections for a formal representative assembly were not permitted), demanding that Lithuanians declare loyalty to Germany and agree to an annexation. The Conference instead announced basic principles of a limited in territorial scope, but independent ethnic Lithuanian state, with cultural rights for the minorities; accordingly, the publication of the Conference's resolution was not allowed. The Conference elected a 20-member Council of Lithuania (Taryba) and empowered it to act as the executive authority of the Lithuanian people. The Council declared on 11 December Lithuanian independence as a German protectorate, and then adopted the outright Act of Independence of Lithuania on 16 February 1918. It proclaimed Lithuania as an independent republic, organized according to democratic principles.
- Bookmark :
- Digg
- del.icio.us
- Stumbleupon
- Redit it
- Posted by - (0) Comment
Independent Lithuania
(1918–1940)
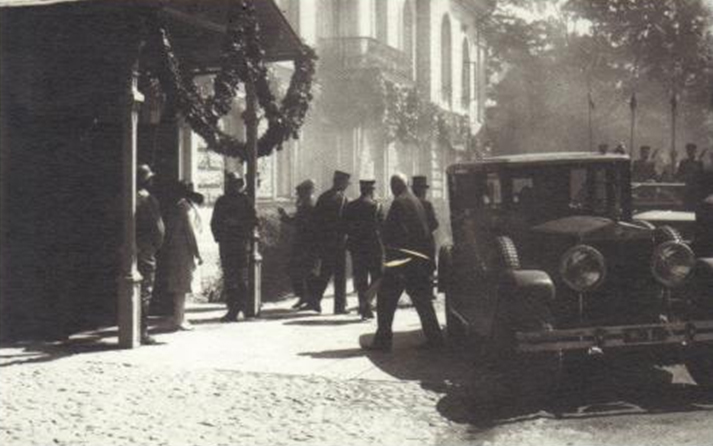

After Vilnius was occupied by the Russian Bolsheviks in 1919, the government of the Republic of Lithuania established its main base in Kaunas. Later, when the capital Vilnius was forcibly annexed by Poland, Kaunas became the temporary capital of Lithuania,a position it held until 28 October 1939, when the Red Army handed Vilnius back to Lithuania. Here a picture from the Presidential Palace of the Republic of Lithuania in Kaunas,
around 1930
At the end of World War I the Germans allowed the Vilnius Conference (18–22 September 1917) to convene (elections for a formal representative assembly were not permitted), demanding that Lithuanians declare loyalty to Germany and agree to an annexation. The Conference instead announced basic principles of a limited in territorial scope, but independent ethnic Lithuanian state, with cultural rights for the minorities; accordingly, the publication of the Conference's resolution was not allowed. The Conference elected a 20-member Council of Lithuania (Taryba) and empowered it to act as the executive authority of the Lithuanian people. The Council declared on 11 December Lithuanian independence as a German protectorate, and then adopted the outright Act of Independence of Lithuania on 16 February 1918. It proclaimed Lithuania as an independent republic, organized according to democratic principles. The Germans, still present in the country, did not support such a declaration and hindered attempts to establish actual independence. To prevent being incorporated into the German Empire, Lithuanians elected Monaco-born King Mindaugas II as the titular monarch of the Kingdom of Lithuania in July 1918. Mindaugas II never assumed the throne.
In the meantime, initially also under the German occupation, an attempt to revive the Grand Duchy of Lithuania as a socialist multinational federal republic took place. Anton Lutskevich and his Belarusian National Council proclaimed in March 1918 the Belarusian People's Republic, which was to stretch from the Baltic to the Black Sea and include Vilnius. Lutskevich and the Council fled the approaching Red Army and left Minsk before it was taken over by the Bolsheviks in December 1918. Upon their arrival in Vilnius, they proposed a Belarusian-Lithuanian federation, which however generated no interest on the part of the Lithuanian leaders, who were in advanced stages of promoting national plans of their own. The Lithuanians were interested only in a state "within ethnographic frontiers", as they perceived it.
Germany lost the war and signed the Armistice of Compiègne on 11 November 1918. Lithuanians quickly formed their first government, led by Augustinas Voldemaras, adopted a provisional constitution, and started organizing basic administrative structures. As the German army, defeated in the West, was withdrawing from the Eastern Front, it was followed by the Soviet forces, whose intention was to spread the global proletarian revolution. They created a number of puppet states, including on 16 December 1918 the Lithuanian Soviet Socialist Republic. By the end of December the Red Army reached Lithuanian borders, starting the Lithuanian–Soviet War.
On 1 January 1919 the German occupying army withdrew from Vilnius turning the city over to local Polish self-defense forces. The Lithuanian government evacuated Vilnius and moved west to Kaunas, which became the temporary capital of Lithuania. Vilnius was captured by the Soviet Red Army on 5 January 1919. As the Lithuanian army was in its infant stages, the Soviet forces moved largely unopposed and by mid-January 1919 controlled about ⅔ of the Lithuanian territory. Vilnius was now the capital of the Lithuanian Soviet Republic, and soon of the combined Lithuanian–Belarusian Soviet Republic.
From April 1919, the Lithuanian–Soviet War went parallel with the Polish–Soviet War. Polish troops captured Vilnius from the Soviets on 21 April 1919. Poland had territorial claims over Lithuania, especially the Vilnius Region, and these tensions spilled over into the Polish–Lithuanian War. Józef Piłsudski of Poland, seeking a Polish-Lithuanian federation, but unable to find common ground with Lithuanian politicians, in August 1919 made an unsuccessful attempt to overthrow the Lithuanian government in Kaunas.
In mid-May the Lithuanian army, commanded by General Silvestras Žukauskas, began an offensive against the Soviets in northeastern Lithuania. By the end of August 1919, the Soviets were pushed out of the Lithuanian territory. The Lithuanian army was then deployed against the paramilitary West Russian Volunteer Army, who invaded northern Lithuania. They were Germany-reactivated and supported German and Russian soldiers who sought to retain German control over the former Ober Ost. West Russian Volunteers were defeated and pushed out by the end of 1919. Thus the first phase of the Lithuanian Wars of Independence was over and Lithuanians could direct attention to internal affairs.
The Constituent Assembly of Lithuania was elected in April and first met in May 1920. In June it adopted the third provisional constitution and on 12 July 1920 signed the Soviet–Lithuanian Peace Treaty. In the treaty the Soviet Union recognized fully independent Lithuania and its claims to the disputed Vilnius Region; Lithuania secretly allowed the Soviet forces passage through its territory, as they moved against Poland.
On 14 July 1920, the advancing Soviet army captured Vilnius for a second time from Polish forces. However, they only handed the city over to Lithuanians on 26 August 1920, following the defeat of the Soviet offensive. The victorious Polish army returned and the Soviet–Lithuanian Treaty increased hostilities between Poland and Lithuania. To prevent further fighting, the Suwałki Agreement was signed on 7 October 1920; it left Vilnius on the Lithuanian side of the armistice line.[58] It had never gone into effect, because Polish General Lucjan Żeligowski, acting on Józef Piłsudski's orders, staged a military action presented as a mutiny. He invaded Lithuania on 8 October 1920, captured Vilnius the following day, and established a short-lived Republic of Central Lithuania on 12 October 1920. The "Republic" was a part of Piłsudski's federalist scheme, which was never to materialize, because of the opposition from both the Polish and Lithuanian (represented now by the Lithuanian government) nationalists. For 19 years, as the Vilnius Region had remained under Polish administration, Kaunas was the temporary capital of Lithuania. The League of Nations attempted to mediate the dispute and Paul Hymans proposed plans of a Polish–Lithuanian union. However, the negotiations broke down as neither side agreed to the compromise. Central Lithuania held a problematic election, boycotted by the Jews, Lithuanians and Belarusians, and was annexed into Poland on 24 March 1922.The Vilnius Region dispute was not legitimately resolved and Lithuania broke all relations with Poland. The two countries were officially at war over Vilnius, the historical capital of Lithuania, inhabited at that time largely by Polish-speaking and Jewish populations, between 1920 and 1938. The dispute continued to dominate Lithuanian domestic politics and foreign policy and doomed the relations with Poland for the entire interwar period.
Democratic Lithuania
The Constituent Assembly, which adjourned in October 1920 due to threats from Poland, gathered again and initiated many reforms needed in the new state: obtained international recognition and membership in the League of Nations, passed the law of land reform, introduced national currency litas, and adopted the final constitution in August 1922. Lithuania became a democratic state, with Seimas (parliament) elected by men and women for a three-year term. The Seimas elected the president. The First Seimas was elected in October 1922, but could not form a government as the votes split equally 38–38, and was forced to resign. Its only lasting achievement was the Klaipėda Revolt from 10-15 January 1923. Lithuania took advantage of the Ruhr Crisis and captured the Klaipėda Region, a territory detached from East Prussia according to the Treaty of Versailles, and placed under French administration. The region was incorporated as an autonomous district of Lithuania in May 1924. For Lithuania it was the only access to the Baltic Sea and an important industrial center. The Revolt was the last armed conflict in Lithuania before World War II. The Second Seimas, elected in May 1923, was the only Seimas in independent Lithuania that served the full term. The Seimas continued the land reform, introduced social support systems, started repaying foreign debt. Strides were made in education: the network of primary and secondary schools was expanded and first universities were established in Kaunas. A national census took place in 1923.
Authoritarian Lithuania
Antanas Smetona, the first and last president of independent Lithuania during the interbellum. The 1918–1939 period if often known as "Smetona's time".
The Third Seimas was elected in May 1926. For the first time Lithuanian Christian Democrats (krikdemai) lost their majority and became an opposition. It was sharply criticized for signing the Soviet–Lithuanian Non-Aggression Pact (Lithuanian claim to Poland-held Vilnius was recognized by the Soviets again)[61] and accused of "Bolshevization" of Lithuania. As a result of growing tensions, the government was deposed during the 1926 Lithuanian coup d'état in December. The coup, organized by the military, was supported by the Lithuanian Nationalists Union (tautininkai) and Lithuanian Christian Democrats. They installed Antanas Smetona as the President and Augustinas Voldemaras as the Prime Minister. Smetona suppressed the opposition and remained as an authoritarian leader until June 1940.
The Seimas thought that the coup was just a temporary measure and new elections should be called to return Lithuania to democracy. The legislative body was dissolved in May 1927. Later that year members of the Social Democrats and other leftist parties, named plečkaitininkai after their leader, tried to organize an uprising against Smetona but were quickly subdued. Voldemaras grew increasingly independent of Smetona and was forced to resign in 1929. Three times in 1930 and once in 1934 he unsuccessfully attempted to return to power. In May 1928 Smetona, without the Seimas, announced the fifth provisional constitution. It continued to claim that Lithuania is a democratic state and vastly increased powers of the President. His party, the Lithuanian Nationalist Union, steadily grew in size and importance. Smetona adopted the title of "tautos vadas" (leader of the nation) and slowly started building personality cult. Many of the prominent political figures married into Smetona's family (Juozas Tūbelis, Stasys Raštikis).
When the Nazi Party came into power in the Weimar Republic, Germany–Lithuania relations worsened considerably as Nazi Germany did not accept the loss of the Klaipėda Region. The Nazis sponsored anti-Lithuanian organizations in the region. In 1934, Lithuania put the activists on trial and sentenced about 100 people, including their leaders Ernst Neumann and Theodor von Sass. That prompted Germany, one of the main trade partners of Lithuania, to declare embargo of Lithuanian products. In response Lithuania shifted its exports to Great Britain. But that was not enough and peasants in Suvalkija organized strikes, which were violently suppressed. Smetona's prestige was damaged and in September 1936 he agreed to call the first elections to Seimas since the coup of 1926. Before the elections all political parties, except the National Union, were eliminated. Thus of the 49 members of the Fourth Seimas, 42 were from the National Union. It functioned as an advisory board to the President and in February 1938 adopted a new constitution, which granted the President even greater powers.
Lithuanian territorial issues 1939-1940
As tensions were rising in Europe following the annexation of Austria by Nazi Germany, Poland presented an ultimatum to Lithuania in March 1938. Poland demanded the re-establishment of normal diplomatic relations, which were broken after the Żeligowski's Mutiny in 1920, and threatened military actions in case of refusal. Lithuania, having a weaker military and unable to enlist international support for its cause, accepted the ultimatum. Lithuania–Poland relations somewhat normalized and the parties concluded treaties regarding railway transport, postal exchange, and other means of communication. Just a year after the Polish ultimatum and five days after the German occupation of Czechoslovakia, Lithuania received as oral ultimatum from Joachim von Ribbentrop demanding to cede the Klaipėda Region to Germany. Again, Lithuania was forced to accept. This triggered a political crisis in Lithuania and forced Smetona to form a new government which for the first time since 1926 included members of the opposition. The loss of Klaipėda was a major blow to Lithuanian economy and the country shifted to the sphere of German influence. When Germany and the Soviet Union concluded the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact in 1939 and divided Eastern Europe into spheres of influence, Lithuania was, at first, assigned to Germany.
- Bookmark :
- Digg
- del.icio.us
- Stumbleupon
- Redit it
The interwar presidents
- Posted by - (0) Comment

Statutes of the three interwar presidents are placed in the park in front of the Historical Presidential Palace in Kaunas. Picture: Statues of Aleksandras Stulginskis (front) and Antanas Smetona.
Photo: Aage Myhre
After Lithuania re-won its freedom in 1918, a Polish military invasion led to an annexation of eastern Lithuania (including the capital city Vilnius) to Poland. This was never recognized and Lithuania remained at a state of war with Poland, with the new government city Kaunas officially designated the “Temporary capital”. “We won’t calm down without Vilnius” became a popular slogan and organizations like the “Union for the Liberation of Vilnius” sprung up with the Lithuanian-Polish territorial dispute becoming one of the keystones of interwar Lithuania’s policy.
- Bookmark :
- Digg
- del.icio.us
- Stumbleupon
- Redit it
The interwar presidents
- Posted by - (0) Comment
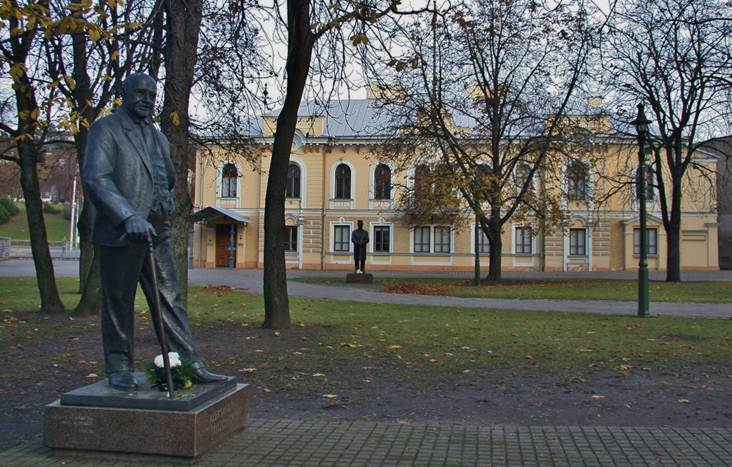

Statutes
of the three interwar presidents are placed in the park in front of the
Historical Presidential Palace in Kaunas. Picture: Statues of Aleksandras
Stulginskis (front) and Antanas Smetona.
Photo:
Aage Myhre
After Lithuania re-won its freedom in 1918, a Polish military invasion led to an annexation of eastern Lithuania (including the capital city Vilnius) to Poland. This was never recognized and Lithuania remained at a state of war with Poland, with the new government city Kaunas officially designated the “Temporary capital”. “We won’t calm down without Vilnius” became a popular slogan and organizations like the “Union for the Liberation of Vilnius” sprung up with the Lithuanian-Polish territorial dispute becoming one of the keystones of interwar Lithuania’s policy.
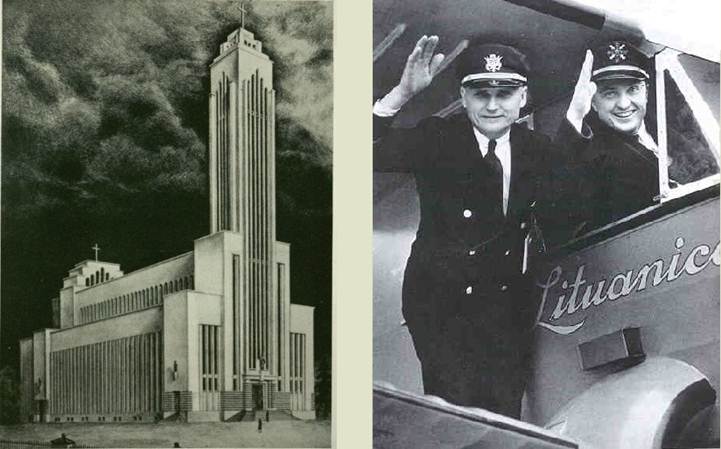

Interwar
Lithuania strived to let the world know of its existence. Left is the art deco
Resurrection church, built to be the largest church in the Baltics and an
important landmark of rapidly expanding Kaunas. Right are Steponas Darius and
Stasys Girėnas, the first Lithuanian pilots to cross the Atlantic (1933). They
subsequently died in air disaster, becoming instant martyrs.
The main western powers recognized Lithuania only in 1922 as they preferred a stronger Poland to counter the German and Soviet threats. But by 1922 it was already clear that the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth would not be reborn as the Poles ceded many eastern lands to the Soviets in the Treaty of Riga.
Unlike the part of Lithuania that was in the Russian Empire, Lithuania Minor remained under German rule except for its northernmost part, the Klaipėda Region (German: Memelland), which was detached from Germany due to its Lithuanian majority. As the Lithuanian Republic was still unrecognized, Klaipėda Region remained under League of Nations rule. In 1923 Lithuania supported a revolt in Klaipėda Region and the new directory (government) of Edmonas Simonaitis joined Lithuania (as a bilingual autonomous area) thereby giving the young country its only seaport. Together with it came a sizeable German minority which caused trouble in the 1930s when the Nazi ideas caught on among the Germans of Klaipėda Region.
1926 saw a military coup with Antanas Smetona retaking presidential power. He ruled until the end of independent Lithuania, the period thus frequently known as the “Smetonic era”. Lithuania became one of the first authoritarian countries in the Eastern Europe, but by the year 1936 only a few, such as Czechoslovakia, would still remain democratic.
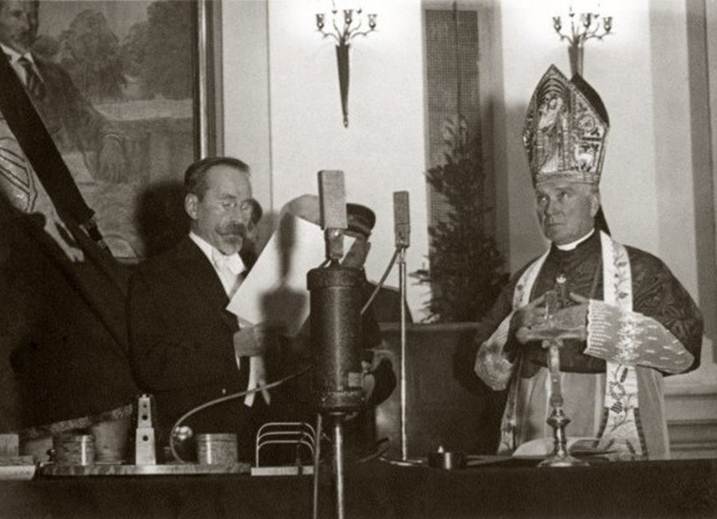

1926:
President Antanas Smetona takes oath before the Catholic bishop.
Interwar Lithuania continued to be an agricultural society with only 20% of people living in cities, therefore it was less heavily hit by the Global Depression, remained a devout Catholic land with the church not disestablished and the birth rates were still high (the population increased by 22% to over 3 million in years 1923-1939 despite the sizeable emigration primarily to the South America).
The foreign policy of Lithuania was friendly to the Germans and Soviets because many other countries, like France or Estonia, supported Poland in the conflict over Vilnius. However, the increasing imperialism of both Germany and the Soviet Union eroded their need for independent Lithuania. In 1939 German ultimatum led to the loss of Klaipėda Region. A secret Molotov-Ribentropp pact protocol included Lithuania in the German zone of influence, but the Smetona’s refusal to invade Poland together with Germany led to the change in the protocol with Lithuania being “ceded” to the Soviet Union. In 1939 Soviet Union established army bases in Lithuania after an ultimatum (this ultimatum also returned 1/5th of Vilnius region, recently occupied by the Soviets during their invasion of Poland), and another ultimatum in 1940 led to a full-scale occupation and annexation.
The interwar presidents
Antanas Smetona
|
|
Date and Place of Birth Family Professional
Qualifications Political, Public, Professional and Cultural Engagement Party Membership In Presidential Office April 6, 1919 – June 19, 1920 December 19, 1926 – June 15, 1940 Soviet occupation After Term of Office |
Alexander Stulginskis
|
|
Alexander Stulginskis (1885 02 26-1969 09 22) He was born Family Professional qualifications The political, social, professional and cultural activities Membership of political parties Office of the President At the end of this term |
Kazys Grinius
|
Kazys Grinius (1866 12 17-1950 06 04) He was born Family Professional qualifications The political, social, professional and cultural activities of Membership of political parties Office of the President At the end of this term |
- Bookmark :
- Digg
- del.icio.us
- Stumbleupon
- Redit it
- Posted by - (0) Comment
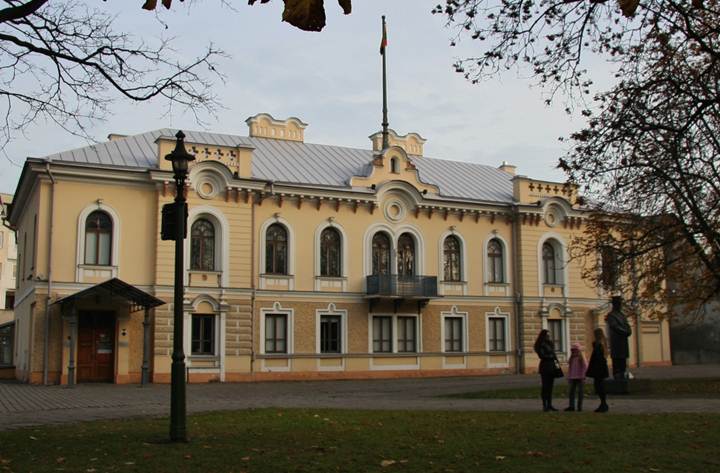
The Presidential Palace
in Kaunas is a must-see

Read more about the Palace at http://www.istorineprezidentura.lt/?lang=en
Photo: Aage Myhre
The Historical Presidential Palace in Kaunas is a must-see place for everyone, whether native-born or a visitor to Lithuania. It is one of the most important memorials of the Republic of Lithuania in 1918–1940.
Visitors are offered an introduction into the evolution of modern Lithuanian statehood, the opportunity to feel the pulse of a growing city that suddenly faced the challenge of becoming a capital and rapidly changed from a fortress into a modern city.
The building was at the centre of major political events of the time. It housed the President’s meetings with the Cabinet, as well as numerous meetings with the representatives of foreign countries, military, clergy and various organizations. It was a fundamental landmark of Foreign Policy; emissaries of foreign states here offered their credentials to the President of the Lithuanian Republic. The building also witnessed the Coup d’état of 1926, a crisis of parlamentarism and a turn towards authoritarian regime. In the face of imminent Soviet occupation, the Last Meeting of the government of the independent Lithuania took place here on the night from June 14 to 15 of 1940.
- Bookmark :
- Digg
- del.icio.us
- Stumbleupon
- Redit it
- Posted by - (0) Comment
The Presidential Palace
in Kaunas is a must-see

Read more about the Palace at http://www.istorineprezidentura.lt/?lang=en
Photo: Aage Myhre
The Historical Presidential Palace in Kaunas is a must-see place for everyone, whether native-born or a visitor to Lithuania. It is one of the most important memorials of the Republic of Lithuania in 1918–1940.
Visitors are offered an introduction into the evolution of modern Lithuanian statehood, the opportunity to feel the pulse of a growing city that suddenly faced the challenge of becoming a capital and rapidly changed from a fortress into a modern city.
The building was at the centre of major political events of the time. It housed the President’s meetings with the Cabinet, as well as numerous meetings with the representatives of foreign countries, military, clergy and various organizations. It was a fundamental landmark of Foreign Policy; emissaries of foreign states here offered their credentials to the President of the Lithuanian Republic. The building also witnessed the Coup d’état of 1926, a crisis of parlamentarism and a turn towards authoritarian regime. In the face of imminent Soviet occupation, the Last Meeting of the government of the independent Lithuania took place here on the night from June 14 to 15 of 1940.
Today the Presidential Palace in Kaunas functions as a memorial-educational institution of Lithuanian modern statehood. The permanent exposition at the Palace reflects the history of the First Republic of Lithuania (1918 – 1940). Periodic temporary exhibitions commemorate outstanding historical figures and events. Many other social and cultural gatherings – such as scholarly conferences, concerts, book presentations, public lectures and meetings with outstanding public persons – are aimed at stimulating discussions about modern statehood and civic society.
Presidential Palace
|
The former residence of the President of the Republic of Lithuania History of the Presidential Palace
|
- Bookmark :
- Digg
- del.icio.us
- Stumbleupon
- Redit it
- Posted by - (0) Comment
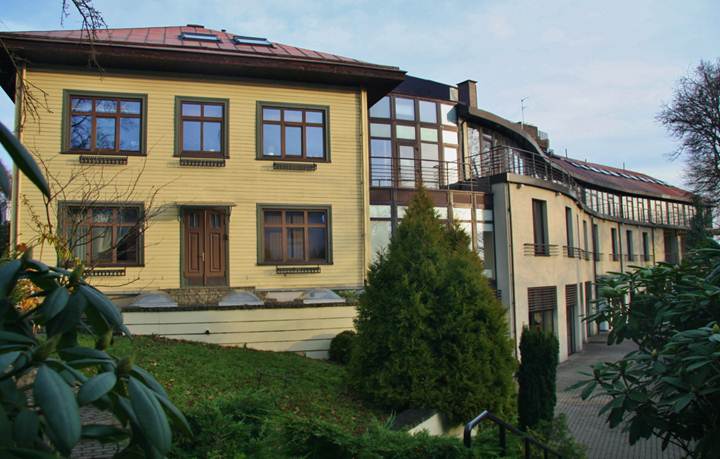
Looking for a hotel in Kaunas?
Try ‘House of Thunder’
(Perkūno Namai)
To read more reviews and book rooms in this or other
Kaunas hotels, go to VilNews Section 22

My preferred hotel in Kaunas. The family owned Hotel Perkūno Namai is beautifully located on a hilltop just outside Kaunas centre, surrounded by an amazingly attractive garden. The house to the left in the picture was built for the family in the 1930s. Perkūno Namai means House of Thunder.
Text and photos: Aage Myhre
Surrounded by centennial oaks Perkūno Namai just outside Kaunas centre has been a family owned and run hotel for 18 years, since 1994. The hotel also includes a high class international restaurant.
The hotel family has its long time roots from up here in Žaliakalnis – the Green Hill – where the site belonged to the present owners grand and great-grandparents. The family house adjoining the hotel was designed in 1930 by a family friend architect, a promoter of functionalism in Lithuania, Vytautas Landsbergis-Žemkalnis (father of today’s famous music professor and politician, Vytautas Landsbergis).
“We are very proud of the hotel’s well-groomed landscape: a rhododendron grove and an oak-tree hillock invigorate our guests, family members and staff all year round,” tells today’s director and co-owner Vidimantas Žekas when I sit down with him for a talk.
- Bookmark :
- Digg
- del.icio.us
- Stumbleupon
- Redit it
- Posted by - (1) Comment
Looking for a hotel in Kaunas?
Try ‘House of Thunder’
(Perkūno Namai)
To read more reviews and book a room in this or other
Kaunas hotels, go to Booking.com on top of this page

My preferred hotel in Kaunas. The family owned Hotel Perkūno Namai is beautifully located on a hilltop just outside Kaunas centre, surrounded by an amazingly attractive garden. The house to the left in the picture was built for the family in the 1930s. Perkūno Namai means House of Thunder.
Text and photos: Aage Myhre
Surrounded by centennial oaks Perkūno Namai just outside Kaunas centre has been a family owned and run hotel for 18 years, since 1994. The hotel also includes a high class international restaurant.
The hotel family has its long time roots from up here in Žaliakalnis – the Green Hill – where the site belonged to the present owners grand and great-grandparents. The family house adjoining the hotel was designed in 1930 by a family friend architect, a promoter of functionalism in Lithuania, Vytautas Landsbergis-Žemkalnis (father of today’s famous music professor and politician, Vytautas Landsbergis).
“We are very proud of the hotel’s well-groomed landscape: a rhododendron grove and an oak-tree hillock invigorate our guests, family members and staff all year round,” tells today’s director and co-owner Vidimantas Žekas when I sit down with him for a talk.
“Our 50-seat restaurant offers creative and stylish cuisine and a quiet atmosphere. My sister Ingrida and I normally welcome our guests personally, treating them to a cup of coffee. We receive our guests as family members and some repeated visitors have become our family friends.”
Mr. Žekas has great pride in his hotel, telling me what one of his recent guests told: “I like this place because once you pass the gate you enter a totally different world under the oak-trees with birds singing above romantic benches surrounded by flowers. It is an Italian court-yard in the middle of Kaunas, a welcoming retreat from the world’s turmoil.”
The hotel includes 29 rooms: 2 deluxe rooms, 6 junior suites, 11 single rooms, and 10 double rooms (with twin beds or a double-bed). All rooms meet international first-class hotel standards. Here you will find everything you need for rest and work: TV sets, direct-dial telephones, mini bars, safe deposit boxes, free wireless internet connection, hair dryers and comfortable en suite bathrooms with heated anti-slip floor. Should you prefer a comfy king size bed, just order it in advance and you will find it ready upon arrival.
Perkūno Namai images
Photos: Aage Myhre


- Bookmark :
- Digg
- del.icio.us
- Stumbleupon
- Redit it
- Posted by - (0) Comment

“Vilnius catches and changes
your soul”
(Daniil Granin, Russian writer)
Go to SECTION 23
TRAVEL LITHUANIA!
__________________________

Bernard Terway
Yes it does - I loved the time I was there, albeit too short.
__________________________

Rolf Hanssen
I lost my heart in Vilnius city
- Bookmark :
- Digg
- del.icio.us
- Stumbleupon
- Redit it
- Posted by - (0) Comment

Butkevičius approved
Lithuania's parliament approved Algirdas Butkevicius as prime minister on Thursday, giving the Social Democrat leader 15 days to present a Cabinet and policy program for approval.
Lawmakers voted 90 to 40 with 4 abstentions to appoint Butkevicius, according to a live broadcast from the parliament in the capital, Vilnius. The 141-seat chamber, which convened this week after October elections, currently only has 139 members as ballots in two districts were declared invalid and will be repeated in March.
The premier-designate's Social Democrat party formed a coalition with the Labor Party, the Order & Justice party and the Lithuanian Polish Election Action. President Dalia Grybauskaite, who proposed Butkevicius for the post and must approve the new government's composition, opposes Labor's participation as it is suspected of fraud and voting violations.
Butkevicius, 54, served as finance minister in 2004-2005 and as transportation minister in 2006-2008. Speaking in parliament earlier this week, he quoted U.S. President Abraham Lincoln, saying the new government would seek to be "for the people" by focusing less on fiscal discipline and more on economic stimulus.
- Bookmark :
- Digg
- del.icio.us
- Stumbleupon
- Redit it
- Posted by - (2) Comment
Kaunas stories from
previous VilNews issues
Former President Valdas Adamkus:
Hiding in the woods near Kaunas
 "I thank my friend Gabrielius Žemkalnis, brother of Vytautas Landsbergis, that I’m still alive. In the years of World War II, he and I joined the resistance movement for Lithuania's independence, together with Leo Grinius, by publishing and circulating the underground, anti-Nazi newspaper “Jaunime, budek!” (Youth, Be on Guard!) in Kaunas.
"I thank my friend Gabrielius Žemkalnis, brother of Vytautas Landsbergis, that I’m still alive. In the years of World War II, he and I joined the resistance movement for Lithuania's independence, together with Leo Grinius, by publishing and circulating the underground, anti-Nazi newspaper “Jaunime, budek!” (Youth, Be on Guard!) in Kaunas.
One day, in 1944, I was suddenly visited by Žemkalnis' sister. She said her brother had been arrested by the Gestapo, but that he had managed to whisper my name to her as he was led out of the apartment. She immediately understood that it was something he and I had together that I had to be warned about. I was still only 17 years old, but realized that this could be extremely serious, so I ran to the woods and hid there for a long time. Read more...
Professor Irena Veisaite:
Escaping from the Kaunas ghetto
 In August 1941 all the Kaunas Jews were imprisoned in the ghetto which was located in the Kaunas suburb Vilijampole. Irena stayed in the ghetto with her grandparents and one aunt. The 7th of November 1943 is a date Irena will never forget. Lithuanian friends of her parents, the Strimaitis family, had managed to convey a message to her in the ghetto, saying that she should follow one of the labour brigades out of the ghetto to the work place in town. They also had procured false documents for her. An agreement was reached with a Jewish policeman who was responsible for the list of workers that she should not be included on the list that day, but still follow the group out and then try to escape unnoticed into a side street as soon as they passed the ghetto gates. The moment of stepping out of the column of Jewish workers was the most horrifying and dangerous one in young Irena's life. But fortunately she made it without being detected. Read more...
In August 1941 all the Kaunas Jews were imprisoned in the ghetto which was located in the Kaunas suburb Vilijampole. Irena stayed in the ghetto with her grandparents and one aunt. The 7th of November 1943 is a date Irena will never forget. Lithuanian friends of her parents, the Strimaitis family, had managed to convey a message to her in the ghetto, saying that she should follow one of the labour brigades out of the ghetto to the work place in town. They also had procured false documents for her. An agreement was reached with a Jewish policeman who was responsible for the list of workers that she should not be included on the list that day, but still follow the group out and then try to escape unnoticed into a side street as soon as they passed the ghetto gates. The moment of stepping out of the column of Jewish workers was the most horrifying and dangerous one in young Irena's life. But fortunately she made it without being detected. Read more...
Attorney Regina Narusiene:
Hiding behind a blue Kaunas curtain
 “I was almost five years old, but I still clearly remember the day when a truck with Soviet soldiers drove up to our home in Kaunas. My father ordered me to hide behind the blue curtains in the home’s living room and not make even the smallest move or sound. Our family was to be deported to Siberia and the soldiers had come to take us. It felt as though it took an eternity before my father returned and told me I could come out from my hiding place. A truck with German soldiers had come up behind the Soviet truck, forcing the Soviets to leave. That probably saved our lives. As the Soviets were returning to Lithuania in 1944 we escaped to Germany, and after living in Displaced Persons camp for 5 years, in 1949 we emigrated to the United States.” Read more...
“I was almost five years old, but I still clearly remember the day when a truck with Soviet soldiers drove up to our home in Kaunas. My father ordered me to hide behind the blue curtains in the home’s living room and not make even the smallest move or sound. Our family was to be deported to Siberia and the soldiers had come to take us. It felt as though it took an eternity before my father returned and told me I could come out from my hiding place. A truck with German soldiers had come up behind the Soviet truck, forcing the Soviets to leave. That probably saved our lives. As the Soviets were returning to Lithuania in 1944 we escaped to Germany, and after living in Displaced Persons camp for 5 years, in 1949 we emigrated to the United States.” Read more...
Dr. Jonas Sliupas:
Declining the presidency (1926)
 The year is 1926. It is a very dark late autumn evening in Kaunas, Lithuania's capital between 1st and 2nd World Wars, when three officers from the Lithuanian army rush up to the house where Dr. Jonas Sliupas now lives while he teaches at the University of Kaunas. It is nearly midnight when the officers knock heavily on his door and asks to come inside. The officers bring shocking news. They tell that since the early autumn of 1926 key officers within two army groups have been in full swing of planning a coup d’état in Lithuania, and that they have now reached the point that they want to depose of President Kazys Grinius and insert a new President. The question to Dr. Sliupas is therefore whether he can accept becoming the country's new President.
The year is 1926. It is a very dark late autumn evening in Kaunas, Lithuania's capital between 1st and 2nd World Wars, when three officers from the Lithuanian army rush up to the house where Dr. Jonas Sliupas now lives while he teaches at the University of Kaunas. It is nearly midnight when the officers knock heavily on his door and asks to come inside. The officers bring shocking news. They tell that since the early autumn of 1926 key officers within two army groups have been in full swing of planning a coup d’état in Lithuania, and that they have now reached the point that they want to depose of President Kazys Grinius and insert a new President. The question to Dr. Sliupas is therefore whether he can accept becoming the country's new President.
But Dr. Sliupas is not willing to accept. Read more...
- Bookmark :
- Digg
- del.icio.us
- Stumbleupon
- Redit it
- Posted by - (0) Comment
|
Crave: An opera without music A chamber opera for four voices at Vilnius Chamber Theatre Saturday 24 November at 19:00 |
|
|
November 24, 2012 at 7:00PM the Vilnius Chamber Theatre will present an evening of British contemporary theatre performed by the actors of Baram Theatre Company - an international theatre company based in the UK and directed by VKT’s artistic director Alicia Gian (USA). Gian’s production of Crave, written by British playwright Sarah Kane, has been conceptualized as “An Opera Without Music” and will be showing for one night only in the capital before it begins touring in theatres throughout the UK in January of 2013. The production was developed in the Spring of 2012 in Exeter, UK by Gian and the actors of Baram Theatre Company who have all previously trained in a psychophysical actor training methodology which combines Asian body/mind training practices - yoga, Indian martial arts, and Tai chi to prepare the actor for score-based performances in which actors respond to images that arise from the dramatic material.
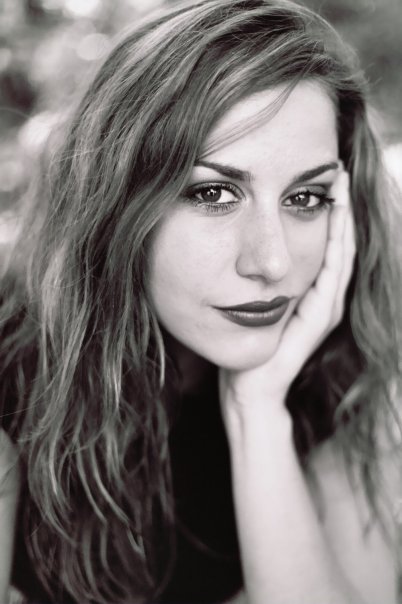

Alicia
Gian
“I hate these words that keep me alive, I hate
these words that won’t let me die...”
-Crave
Sarah Kane (1971-1999) was a young, dynamic, and controversial playwright, whose words were immortalized when she committed suicide at the age of 28. During the 1990’s, when drama in the UK was shifting away from the conventions of naturalist theatre, Kane emerged as the quintessential In-Yer-Face British drama playwright, creating provocative dramatic material that required the audience to look up close at issues that generate discomfort. She created an experiential theatre of sensation which challenges the distinctions that define who we are: right/wrong, animal/human, good/evil, art/life, normal/abnormal - binary oppositions that are central to our world view. Her first three plays: Phaedra’s Love, Blasted, and Cleansed were marked by considerable on-stage violence, but her fourth play Crave, written under the pen name Marie Kelvedon (Marie her middle name and Kelvedon the town where she was raised) so that the piece would not be tainted by the playwright’s notorious reputation nor by the fact that she considered the play unfinished at the time of performance (it remained unfinished), was the beginning of her experimentation with a freer, fragmented, and more lyrical form of writing which characterizes the last two and most personal of her plays: Crave and Psychosis 4:48. Kane wrote Crave, which is considered to be one of the more complex plays of the 1990’s, when she had “lost her faith” in love. The themes and images of damaged lives are explored through the fragmented inner journeys of four characters A, B, C and M - four disintegrating minds under the pressures of love, loss and desire.
“I don’t have music, Christ I wish I had music but all I have is words...” - Crave
Gian, the play’s director and a classically trained singer, explains how she structurally approached the fragmented and non-linear text: “Kane offers no setting, no stage directions and no indication of actions in the play and considered it an experiment with the rhythm and musicality of language; therefore we worked with the text as if it were an opera score comprised of arias and oratorios - a chamber opera for four voices. Sections of the text were divided according to recurring themes and motifs, but instead of singing with the voice, the actors “sung” with their bodies by developing movement scores activated by images that arose organically from the text and developed in rehearsal. The actors trained in operatic breathing techniques for four weeks before any staging of the text began. The goal was to learn to breathe together and allow the breath - just as it does in singing - to sculpt the shape of the thought through movement and text.”
“I keep coming back...again and again...the eternal return...” - Crave
Crave is considered to be Kane’s most personal text and also an ambitious attempt at recasting theatrical form. It is permeated with allusions from the Bible as well as Shakespeare and T.S. Elliot’s “The Wasteland”, but Gian and the actors of Baram primarily explored the text through the Buddhist concept of Tanhā - translated as a craving or thirst and is comprised of three essential stages: the desire of having, the desire of becoming, and the desire of escaping. “As we studied the text we identified each character’s fluxuations between these three stages of desire as described in Buddhist philosophy. This allowed the actors to chart the course of their character’s spiritual journey amongst the fragmented and harsh terrain of the text.”
Gian and Baram Theatre are currently staging Sarah Kane’s other one act play, Psychosis 4:48, which is planned to premiere alongside Crave in the Summer of 2013 in the UK.
Tickets are available through Bilietai.lt and at the door.
Doors open at 6:30 to the public
After the show the audience is invited to stay for a glass of wine to meet the actors and discuss the performance.
Vilnius Chamber Theatre is located at 23 Konstitucijos Prospect - directly across the street from the National Art Gallery.
For more information please visit: www.vkamerinisteatras.lt
- Bookmark :
- Digg
- del.icio.us
- Stumbleupon
- Redit it
- Posted by - (0) Comment

Vilnius
Where old meets new
"Art may be a particularly good medium for distilling and reflecting the characteristics of a nation, but contemplation of it does not give us the vivid and visceral experience of them that we may crave," as Alain de Botton wrote recently in BA’s Highlife magazine.
"We’re learning that what we might really want to do is to talk to people," the philosopher continued, with his usual — and irresistible — knack for nailing ideas so simple you wonder why nobody had nailed them before. "This is remarkably hard."
Our increasing desire for stories, for the sweet sensation of living and breathing a city rather than digesting its historical data, hit me afresh in Vilnius.
Lithuania’s capital is a gem. Its Old Town is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. It was a European Capital of Culture in 2009. It’s a small place by any measure, but one spilling over with Gothic, Baroque and Renaissance churches, town halls and other buildings.
Yet none of these things puts the hook in me. What puts the hook in me is the moment I wander into a small chapel above the Gate of Dawn to find a wedding underway. An older couple exchanges vows — she in a cream bonnet, he with a bouquet of blooms under his arm and trousers bunching around his ankles. A Handycam is propped atop of the organ.
Beneath vaulted ceilings, a priest in a golden robe takes a step backwards. The couple leans in together and delivers a quick, bird-like kiss. The small crowd around them claps.
And there it is. Interesting and all as the 16th century Gate of Dawn is, or the fact that its famous icon of the Virgin Mary is said to have healing powers, or that Pope John Paul II took time to say the rosary here in 1993, the strongest memory I’m taking away is of that little kiss.
That moment in time. That stolen insight into two Lithuanian lives…
Read more…
- Bookmark :
- Digg
- del.icio.us
- Stumbleupon
- Redit it
- Posted by - (0) Comment
Vilnius
|
Pól Ó Conghaile, Irish Examiner
"Art may be a particularly good medium for distilling and reflecting the characteristics of a nation, but contemplation of it does not give us the vivid and visceral experience of them that we may crave," as Alain de Botton wrote recently in BA’s Highlife magazine. "We’re learning that what we might really want to do is to talk to people," the philosopher continued, with his usual — and irresistible — knack for nailing ideas so simple you wonder why nobody had nailed them before. "This is remarkably hard." Our increasing desire for stories, for the sweet sensation of living and breathing a city rather than digesting its historical data, hit me afresh in Vilnius. Lithuania’s capital is a gem. Its Old Town is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. It was a European Capital of Culture in 2009. It’s a small place by any measure, but one spilling over with Gothic, Baroque and Renaissance churches, town halls and other buildings. Yet none of these things puts the hook in me. What puts the hook in me is the moment I wander into a small chapel above the Gate of Dawn to find a wedding underway. An older couple exchanges vows — she in a cream bonnet, he with a bouquet of blooms under his arm and trousers bunching around his ankles. A Handycam is propped atop of the organ. Beneath vaulted ceilings, a priest in a golden robe takes a step backwards. The couple leans in together and delivers a quick, bird-like kiss. The small crowd around them claps. And there it is. Interesting and all as the 16th century Gate of Dawn is, or the fact that its famous icon of the Virgin Mary is said to have healing powers, or that Pope John Paul II took time to say the rosary here in 1993, the strongest memory I’m taking away is of that little kiss. That moment in time. That stolen insight into two Lithuanian lives… |
- Bookmark :
- Digg
- del.icio.us
- Stumbleupon
- Redit it
- Posted by - (0) Comment
This week in politics
 |
New parliament sworn in Lithuania's new Seimas (parliament), elected last month, assembled for its first sitting on Friday 16 November. Read more… |
 |
The President did not show up All previous presidents always personally welcomed new deputies of the Seimas at their first session. Read more… |
 |
But the ex-President did Former Lithuanian President Valdas Adamkus says he is hopeful about the country's new Seimas. Read more… |
 |
Court adjourns hearing Vilnius Regional Court was this week scheduled to hear the Labour Party's fraudulent bookkeeping case, but… Read more… |
 |
New parliament speaker? Lithuania's Labour Party will propose Vydas Gedvilas for the post of parliamentary speaker. Read more… |
 |
President not yet ready President Dalia Grybauskaitė not yet ready to nominate Social Democratic Algirdas Butkevičius as new PM. Read more… |
 |
Uspaskich to leave Brussels The Labour Party's leader has decided to give up his mandate as a member of the European Parliament. Read more… |
 |
Polish party to head energy? Leader of the Electoral Action of Poles, Valdemar Tomaševski, remains secretive. Read more… |
- Bookmark :
- Digg
- del.icio.us
- Stumbleupon
- Redit it
- Posted by - (0) Comment
|
|
|
|
|
|
By Jon Platakis, National Lithuanian American Hall of Fame
Electricity filled the air as the audience packed the main hall of the Balzekas Museum of Lithuanian Culture in Chicago, Illinois on Saturday, November 3, 2012.
As Jon Platakis, founder and chairman of the National Lithuanian American Hall of Fame which sponsored the event, began his introduction, first, second, and third generation Lithuanian Americans, along with a contingent of students from Daley College, sat in eager anticipation.
- Bookmark :
- Digg
- del.icio.us
- Stumbleupon
- Redit it
VilNews e-magazine is published in Vilnius, Lithuania. Editor-in-Chief: Mr. Aage Myhre. Inquires to the editors: editor@VilNews.com.
Code of Ethics: See Section 2 – about VilNews. VilNews is not responsible for content on external links/web pages.
HOW TO ADVERTISE IN VILNEWS.
All content is copyrighted © 2011. UAB ‘VilNews’.

 Click on the buttons to open and read each of VilNews' 18 sub-sections
Click on the buttons to open and read each of VilNews' 18 sub-sections 







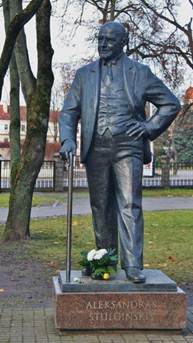



















.jpg)



